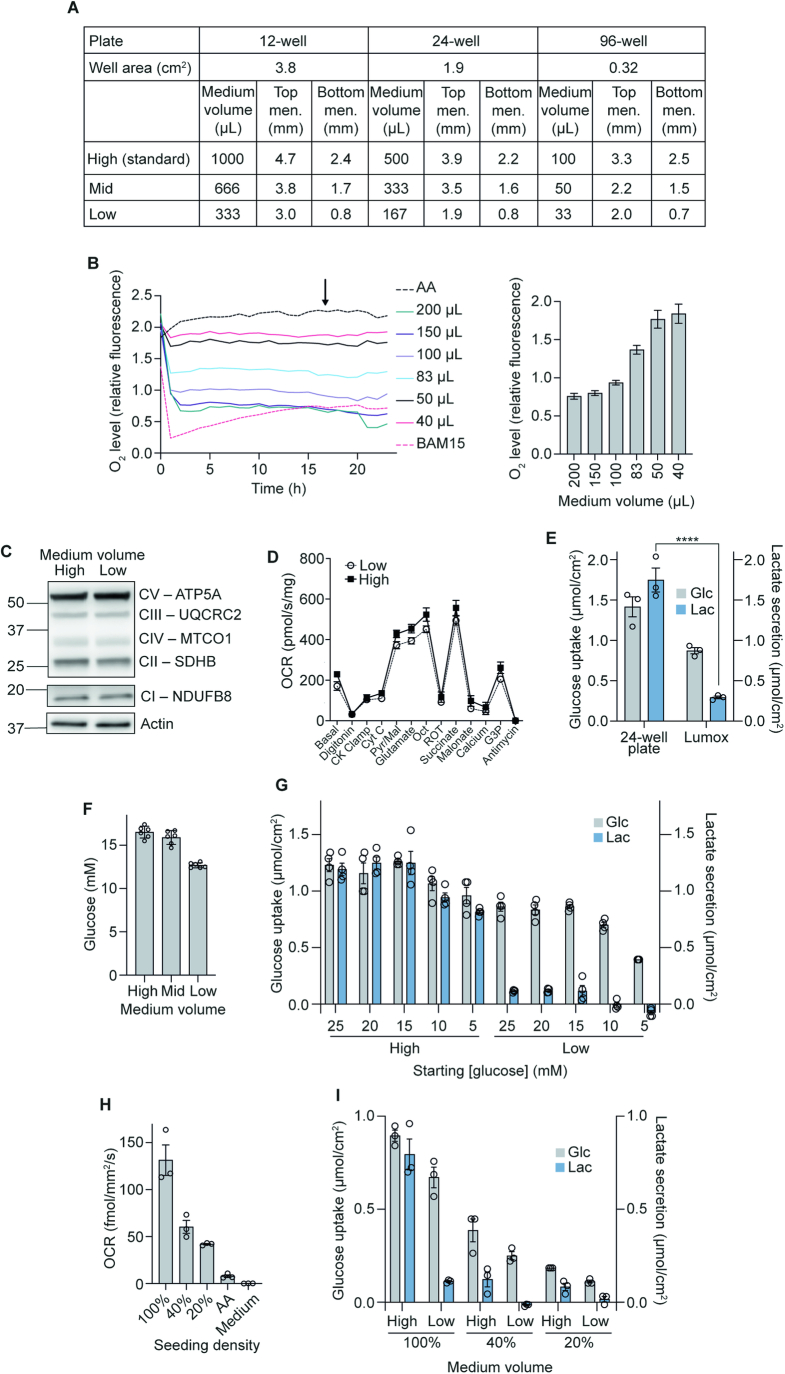
Figure EV1. Changes in glucose metabolism in low medium is due to increased oxygen availability.
(A) Table of medium volumes used in this study and the corresponding medium heights of both top and bottom menisci. Images of each plate-type containing different medium volumes were used to measure menisci heights. Known well diameters were used to convert menisci heights from pixels to mm. ‘High’ refers to the standard culture volumes used. (B) Representative trace of fluorescence intensity indicative of pericellular oxygen concentrations under different medium volumes, measured for 24 h in 96-well plates. The bar graph shows relative oxygen levels taken at 16 h (arrow in representative trace) (n = 4 biological replicates). AA antimycin A. (C) Western blot of mitochondrial respiratory complexes I–V after 16 h of medium volume change in 12-well plates (n = 3 biological replicates). (D) Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) of permeabilised 3T3-L1 adipocytes upon different substrate stimulation after 16 h of medium volume change (n = 5 biological replicates). (E) Extracellular medium glucose and lactate measurements in 24-well or Lumox plates after 16 h culture in high or low medium volumes (n = 3 biological replicates). (F) Medium glucose concentration after 16 h of medium volume change in 12-well plates (n = 6 biological replicates). (G) Extracellular medium glucose and lactate measurements after 16 h medium volume change with different starting glucose concentrations in 12-well plates. (n = 4 biological replicates). (H) OCR measurements from different cell densities in 96-well plates (n = 3 biological replicates). (I) Extracellular medium glucose and lactate measurements after 16 h medium volume change with different cell densities in 12-well plates measured by DNA concentration. (n = 3 biological replicates). Data information: Data were represented as mean ± SEM (B, D–I). ****p < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA with Šidák correction for multiple comparisons (E).