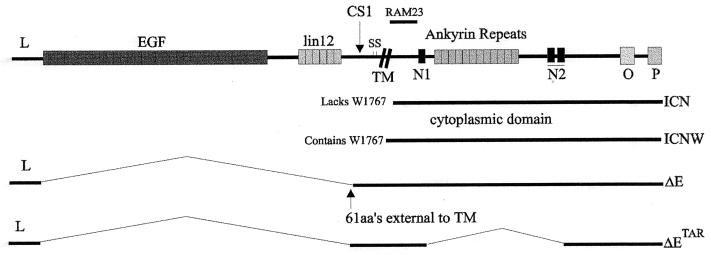
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram showing the full-length NOTCH1 protein with the identified extracellular and intracellular domains. The epidermal growth factor-like repeats and the lin-12-like repeats are positioned extracellular to the transmembrane domain. Two cysteine repeats are potentially involved in the formation of disulfide bridges. The cdc10 (ankyrin) repeats, the two nuclear localization signals (N1 and N2), and the PEST (P) and OPA (O) sequences are intracellular domains (6). The ΔE construct contains the leader peptide, the transmembrane domain, and the intracellular region of NOTCH1 and localizes to the nuclear membrane. The ICN construct lacks the leader peptide and the transmembrane region and localizes to the nucleus. The ΔETAR construct contains the same sequence as ΔE but lacks the ankyrin repeats (3). ICNW contains the entire intracellular domain, including W1767 that is crucial for RBP-Jκ association (3).