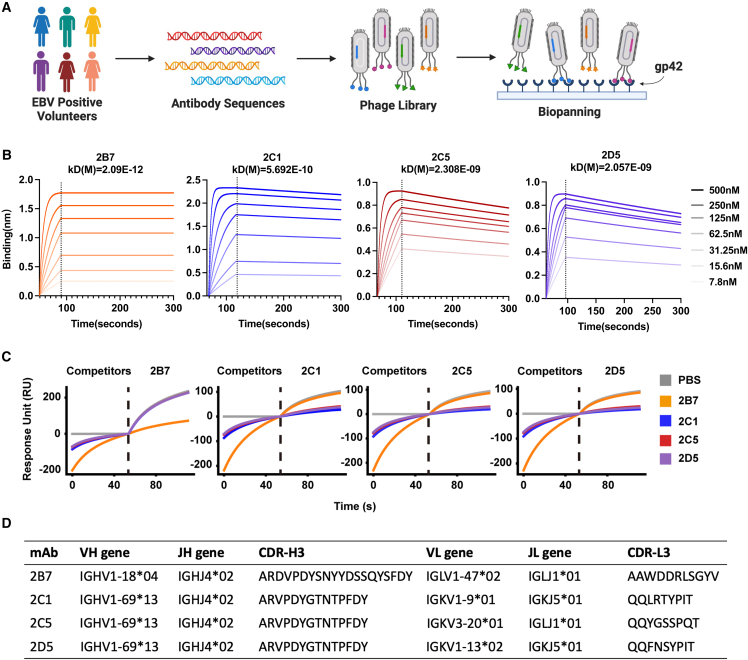
Figure 1.
Isolation and identification of anti-gp42 antibodies
(A) Schematic representation of the phage library generation and screening process. Peripheral blood samples were collected from EBV-positive volunteers. DNA fragments encoding the variable region of the B cell receptor domain were amplified and incorporated into the phage genomes. Following three rounds of screening on immobilized gp42, phages bound to gp42 were isolated and subjected to sequencing.
(B) Measurement of binding kinetics by bio-layer interferometry (BLI) assay for purified 2B7, 2C1, 2C5, and 2D5. KD represents the equilibrium dissociation constant. The biotin-conjugated gp42 protein was immobilized on SA sensors. The range of antibody concentrations was from 500 to 7.8 nM.
(C) Competition assay of purified antibodies (2B7, 2C1, 2C5, and 2D5) using surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
(D) Antibody characteristics of 2B7, 2C1, 2C5, and 2D5. CDRs are defined using the IMGT numbering scheme.28
See also Figure S1.