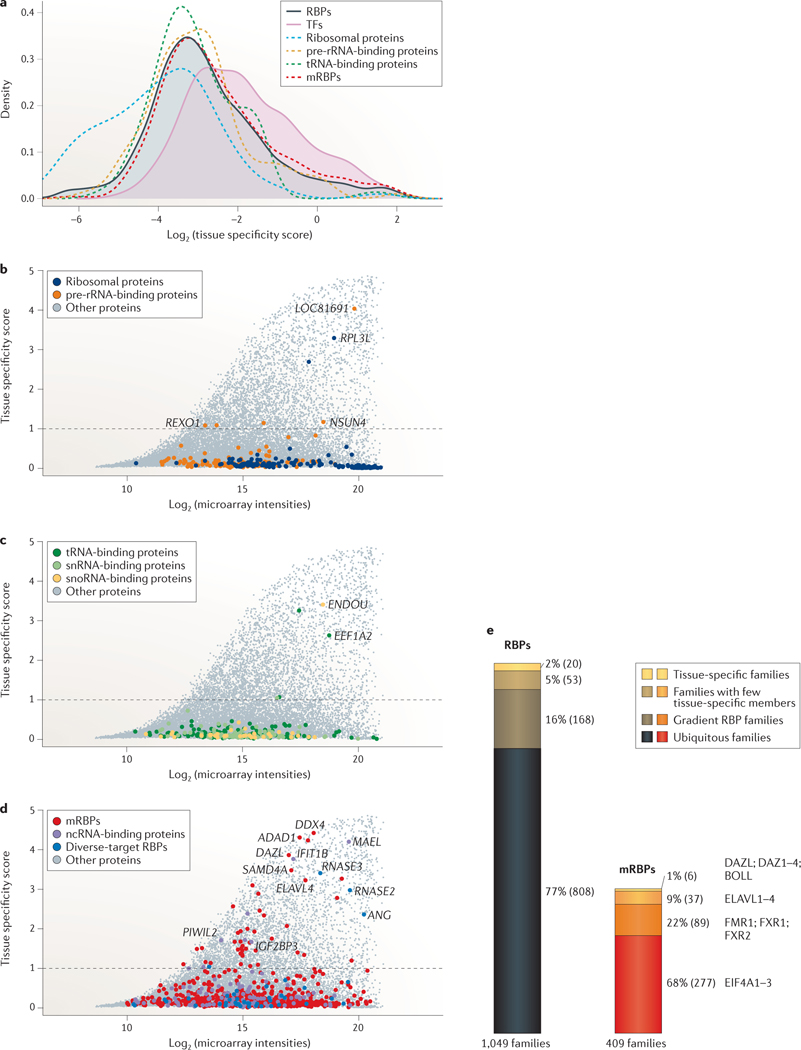
Figure 5 |. Tissue specificity of RBPs across 31 human tissues and organs.
A tissue specificity score was calculated from mRNA expression levels of 1,441 RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and 1,463 transcription factors (TFs) profiled in a human microarray tissue atlas assessing expression across 31 tissues96. a | Densities of the log2-transformed tissue specificity scores are shown for RBPs, TFs, ribosomal proteins, mRNA-binding proteins (mRBPs), as well as tRNA- and pre-ribosomal RNA-binding proteins. The densities of RBPs and TFs are filled in shades to highlight their shifts in distribution. b | Log2 maximum expression intensity values of a gene versus tissue specificity scores for ribosomal proteins and pre-rRNA-binding proteins are compared with that of the residual proteome. Tissue-specific genes were defined as genes with scores ≥1 (dashed line). Selected genes are highlighted. c | A similar analysis is shown for tRNA-, small nuclear RNA (snRNA)- and small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA)-binding proteins. d | Same as part b for mRBPs, non-coding RNA (ncRNA)-binding proteins and diverse-target RBPs. e | Expression of 1,049 paralogous RBP families, of which 409 are mRBP families, is profiled in the tissue atlas (scaled to relative size). Families are grouped into different categories of expression. Representative paralogous families are highlighted for mRBPs. A total of 2% of RBPs and 1% of mRBP families displayed tissue-specific expression for all their members; 5% of RBPs and 9% of mRBP families had one or more members with tissue specificity scores ≥1. 16% of RBPs and 22% of mRBP families had members with tissue-specificity scores ranging between 0.3 and 1, classified here as gradient RBP families, and 77% of RBPs and 68% of mRBP families displayed little variation in expression (tissue specificity scores <0.3), which are referred to as ubiquitous RBP and mRBP families, respectively.