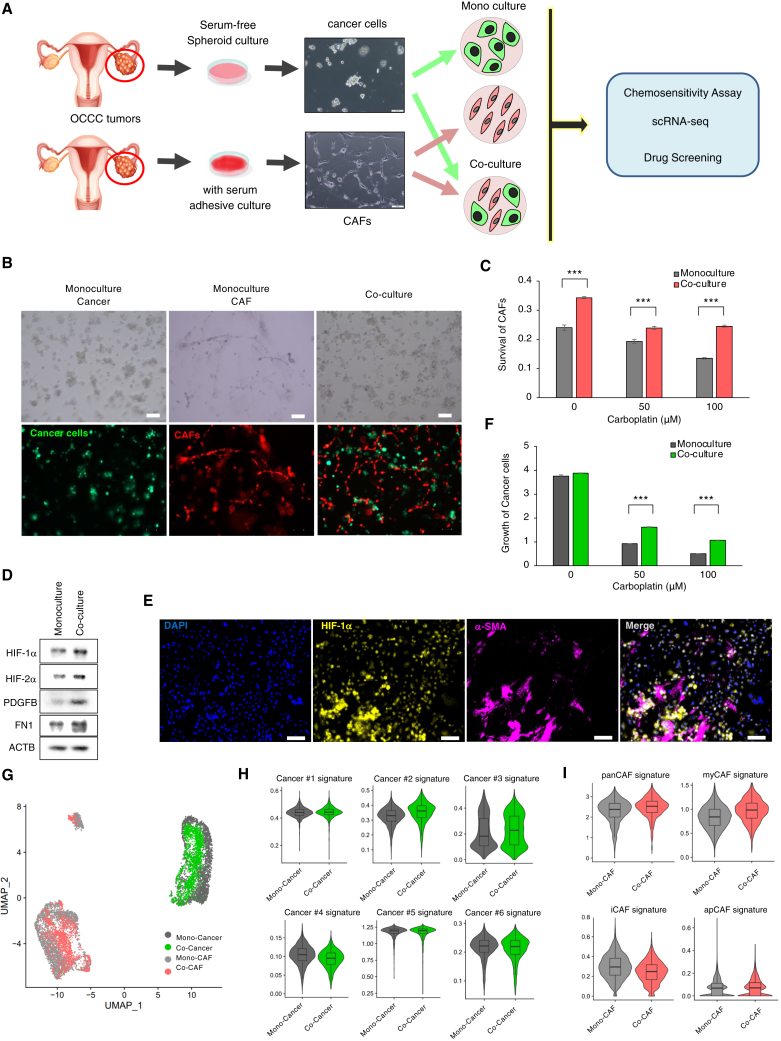
Figure 5.
Co-cultivation of CAFs with chemoresistant OCCC cells recapitulates the chemoresistant niche in vitro
(A) Experimental design of the in vitro co-culture system. Cancer spheroid cells and CAFs were derived from surgical specimens of HIF-1α-positive OCCC. The established cancer cells and CAFs were labeled with GFP/Luc2 and mCherry/hRluc, respectively; cultivated either alone or in combination; and subjected to a chemosensitivity assay, scRNA-seq, or drug screening.
(B) Bright-phase images (top) and fluorescence images (bottom) of the indicated cells cultivated under organoid conditions for 7 days. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(C) Survival of CAFs upon monoculture or co-culture with cancer cells (OVN-48) for 7 days. Cultured cells were grown in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of carboplatin, and cell survival was evaluated by measuring hRLuc activity. The data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). p values were determined by Student’s t test. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(D) Western blot analyses of cancer cells that were sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) after incubation under monoculture or co-culture conditions for 3 days.
(E) Representative image of immunostaining of HIF-1α and α-SMA in cancer cells and CAFs co-cultured for 3 days. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(F) Cancer cell growth (OVN-48) upon monoculture or co-culture with CAFs for 7 days. Cultured cells were grown in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of carboplatin, and cancer cell proliferation was evaluated by measuring Luc2 activity (n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(G) UMAP plot of scRNA-seq data from cancer cells (OVN-48) and CAFs incubated under monoculture and co-culture conditions for 3 days.
(H) Violin plots of the signature scores for the cancer subpopulations (Cancer #1–6) grown under the monoculture and co-culture conditions in (G).
(I) Violin plots of the indicated signature genes in CAFs grown under the monoculture and co-culture conditions shown in (G). Statistically significant differences are indicated: ∗∗∗p < 0.001.