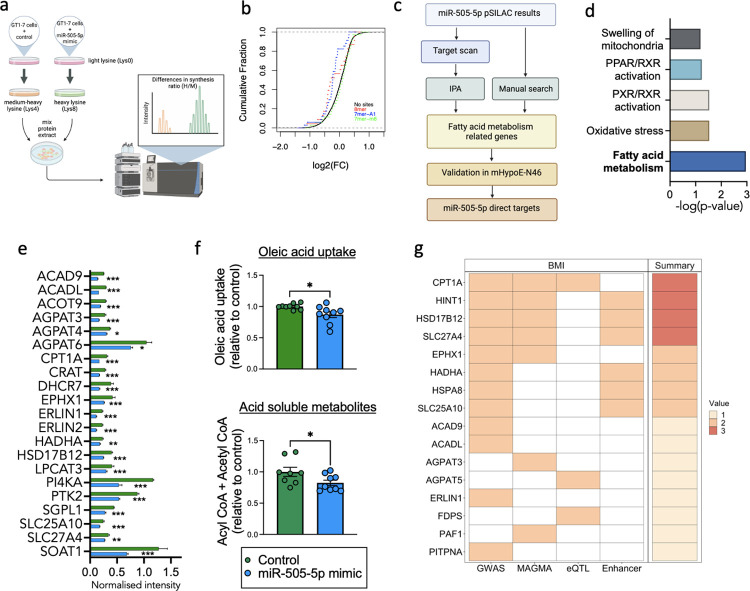
Fig 3. miR-505-5p targets are involved in FA metabolism and genetically associated with BMI in humans.
(a) Diagram of pulsed SILAC experiment in GT1-7 cells to identify targets of miR-505-5p. (b) Cumulative fraction analysis of lys8-labelled: lys4-labelled proteins ratio according to occurrence and type of mRNA binding site for miR-505-5p, as predicted by TargetScan (v. 7.2). (c) Workflow used to identify direct targets of miR-505-5p. (d) Top regulated pathways among miR-505-50 direct targets as reported in IPA. (e) miR-505-5p target proteins of interest identified through IPA and manual search of pSILAC data. (f) Radiolabelled oleic acid metabolism into acid-soluble metabolites and oleic acid uptake in mHypoE-N46 following transfection with either a miR-505-5p mimic or control for 48 h. (g) Heatmap showing the overlap between human orthologs of identified miR-505-5p FA metabolism-related target genes in mice and human genetic datasets. Target genes were annotated on the basis of (i) proximity to GWAS signals, (ii) aggregate gene-level associations to the trait, (iii) colocalization between the GWAS and eQTL data, and (iv) the presence of known enhancers within the GWAS signals. Total number of the observed concordant predictors (out of 4) is displayed in the summary panel. Expanded results can be found in S4 Table. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired T test. The underlying data are provided as S1 Data file. BMI, body mass index; eQTL, expression quantitative trait loci; FA, fatty acid; GWAS, genome-wide association study; IPA, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis.