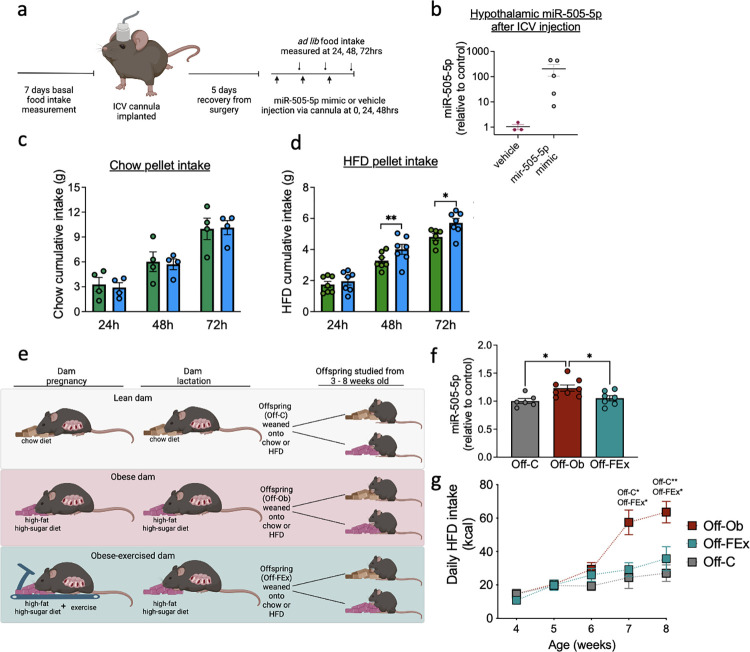
Fig 5. ICV injection of miR-505-5p in adult mice increases intake of an HFD, while a maternal exercise intervention corrects offspring hypothalamic miR-505-5p levels and reduces intake of an HFD.
(a) Diagram depicting surgical schedule. Mice were allowed to recover for 5 days post-implanted of an ICV cannula into the lateral ventricle. Mice then received injection of either a vehicle or miR-505-5p mimic into the ICV cannula and food intake was measured over 3 days. (b) qPCR confirming overexpression of miR-505-5p in the hypothalamus after ICV injection of miR-505-5p mimic. (c) Chow diet cumulative food intake after 3 consecutive days of treatment (24–1 dose, 48–2 doses, and 72 h—3 doses—after first treatment). (d) HFD cumulative food intake after 3 consecutive days of treatment (24–1 dose, 48–2 doses, and 72 h—3 doses—after first treatment). (e) Graphical depiction of maternal obesity model with third group of dams that underwent moderate exercise intervention during obese pregnancy. (f) Relative expression of miR-505-5p in the arcuate nucleus of 8-week-old male offspring born to control, obese or obese-exercised dams. (g) HFD pellet daily kilocalorie intake of male offspring born to control, obese or obese-exercised dams. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired T test (c and d), one-way ANOVA (f), and mixed effects analysis with Sidak post hoc test (g). The underlying data are provided as S1 Data file. HFD, high-fat diet; ICV, intra-cerebroventricular.