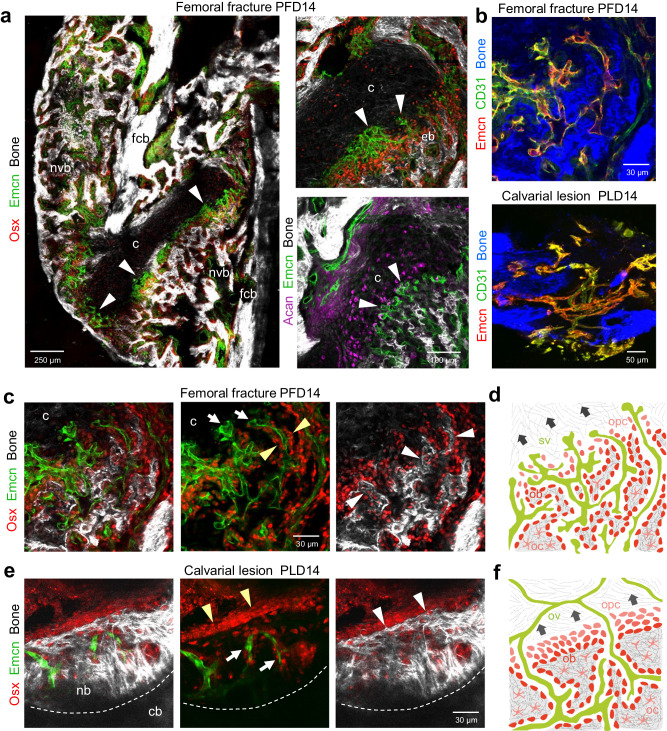
Fig. 6. Vascular and bone regeneration in femoral fractures and calvarial bone lesions.
a Tile-scan multiphoton microscopy of a PFD14 femoral fracture. Overview image shows maximum intensity projections of Emcn+ (green) microvasculature, Osx+ (red) osteoblasts and progenitors and SHG+ (white) newly formed trabecular-like woven bone (ntb) and fractured compact bone (fcb). Zoom-in views (right) show early Emcn+ microvessels (arrowheads) invading the Acan+ (purple, aggrecan) cartilage (c) in close proximity to Osx+ osteoprogenitors. Early SHG+ bone matrix depositions (eb) at the chondro-osseous junction. White arrowheads indicate bud-shaped vascular sprouts. b Multiphoton microscopy showing Emcn+ (red) and CD31+ (green) microvessels at the chondro-osseous junction of a femoral fracture at PFD14 (top) and of a calvarial lesion at PLD14 (bottom). c Multiphoton microscopy of femoral fracture at PFD14 showing Emcn+ microvessels in adjacent Osx+ osteoprogenitors. White arrows point to bud-shaped microvessels invading cartilaginous tissue (c). Early finger-shaped SHG+ bone matrix deposits (white arrowheads). Yellow arrowheads point to osteoblasts adjacent to early bone matrix deposits. d Schematic representation of the process of endochondral ossification after femoral fracture with sprouting vessels (sv) invading the hypertrophic cartilage at the chondro-osseous junction. Osteoprogenitors (opc) co-migrate in close proximity to the invading vessels. Osteoprogenitors differentiate into early osteoblasts (ob) that deposit collagen fibers and trabecular-like bone matrix. Osteoblast that are enclosed by bone matrix differentiate to osteocytes (oc). Dark arrows indicate the direction of the ossification process. e Multiphoton microscopy of PLD14 calvarial bone lesion showing Emcn+ microvessels, multicellular layer of Osx+ osteoblasts and progenitors leading the SHG+ growing bone edge. White arrowheads point to SHG+ growing bone edge. Yellow arrowheads point to multicellular layer of Osx+ osteoblasts and progenitors. f Schematic representation of the process of intramembranous ossification after calvarial lesion injury with osteoblastic cells collectively invading the vascularized lesion tissue as a multicellular layer. Osteoprogenitors (opc) differentiate into osteoblasts (ob) and form new bone matrix. Blood vessels in the lesion are either remodeled or surrounded by the growing bone. Specialized osteogenic vessels (ov) are located close to the growing bone front. Dark arrows indicate the direction of the ossification process. Reproducibility was ensured by n = 3 or more biologically independent experiments.