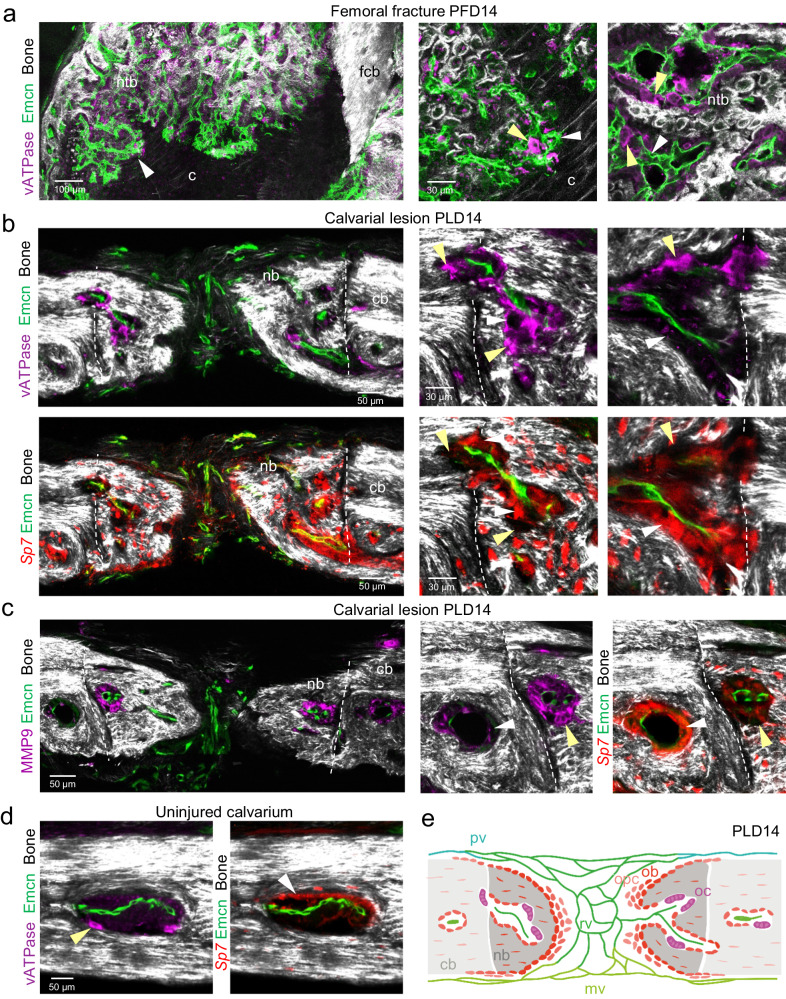
Fig. 7. Bone remodeling by osteoclasts in femoral fractures and calvarial bone lesions.
a Tile-scan multiphoton microscopy of PFD14 femoral fracture. Overview image shows maximum intensity projections of Emcn+ (green) microvasculature, vATPase+ (purple) osteoclasts and SHG+ (white) newly formed trabecular-like woven bone (ntb) and fractured compact bone (fcb). Zoom-in views show vATPase+ osteoclasts (yellow arrowhead) in close association with early Emcn+ microvessels (white arrowhead) invading the cartilage (c) at the chondro-osseous junction (middle) and vATPase+ osteoclasts in close association with remodeling Emcn+ microvessels and early SHG+ bone matrix deposition (right). b Multiphoton microscopy showing vATPase+ osteoclasts (top) and Sp7+ osteoblasts (bottom) together with Emcn+ microvessels residing in small cavities of newly formed SHG+ calvarial bone at PLD14. Yellow arrowheads point to vATPase+ osteoclasts located near SHG+ bone. White arrowheads point to osteoblasts located at complementary locations compared to osteoclasts. c Multiphoton microscopy showing MMP9+ staining and Emcn+ microvessels in calvarial bone lesion of PLD14. Note that MMP9+ staining is associated with multinucleated cells of osteoclast morphology (yellow arrowhead) located close to SHG+ bone. White arrowhead indicates Sp7+ osteoblasts located at complementary locations to MMP9 staining. d Multiphoton microscopy showing vATPase+ osteoclasts (left) and Sp7+ osteoblasts (right) together with Emcn+ microvessels in BM cavities of uninjured calvarial bone. e Schematic showing the process of intramembranous ossification after calvarial lesion injury with osteoblastic cells collectively invading the vascularized lesion tissue as a multicellular sheet. Newly formed bone cavities contain microvessels together with bone-forming osteoblasts (ob) and bone-resorbing osteoclasts at complementary locations, suggesting that cavities in newly formed bone are actively remodeling. opc osteoprogenitors, ob osteoblasts, oc osteoclasts, rv remodeling vessels, mv meningeal vessels, pv periosteal vessels. Reproducibility was ensured by n = 3 or more biologically independent experiments.