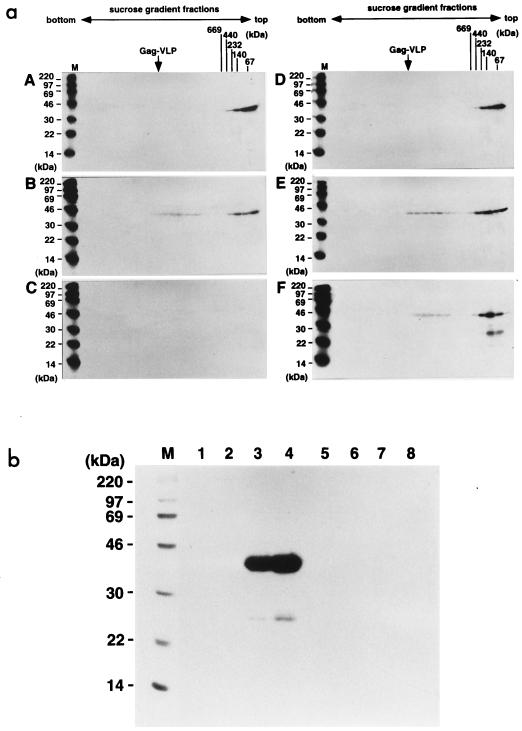
FIG. 6.
Time courses of multimerization for myristoylated and nonmyristoylated Gag proteins and incorporation into Gag VLPs. Sf9 cells expressing wild-type MA-CA-p2 and nonmyristoylated MA(G2A)-CA-p2 proteins were pulse-labeled with a [35S]methionine-cysteine mixture for 10 min and then chased for the indicated time with an excess of unlabeled amino acids. (a) Sedimentation profiles of the soluble Gag proteins purified from the cells at each chase period. Following sedimentation, fractions of 20 to 70% sucrose gradients were collected from the bottom to the top (left to right) and subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by fluorography. A to C, wild-type MA-CA-p2 protein; D to F, nonmyristoylated MA(G2A)-CA-p2 protein. A and D, 0-h chase; B and E, 3-h chase; C and F, 6-h chase. Positions of high-molecular-weight calibration markers (described in the legend to Fig. 4) sedimented in parallel and of wild-type Gag VLP (arrow) are indicated. Lanes M show 14C-labeled molecular weight markers for SDS-PAGE (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech). (b) Time course of Gag VLP production. Gag VLPs were purified from the culture media at each chase point and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by fluorography. Lanes: M, 14C-labeled molecular weight markers for SDS-PAGE (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech); 1 to 4, Gag VLP fractions of wild-type MA-CA-p2; 5 to 8, Gag VLP fractions of nonmyristoylated MA(G2A)-CA-p2; 1 and 5, 0-h chase; 2 and 6, 3-h chase; 3 and 7, 6-h chase; 4 and 8, 9-h chase.