Figure 3. R-Loop formation is the rate-limiting step.
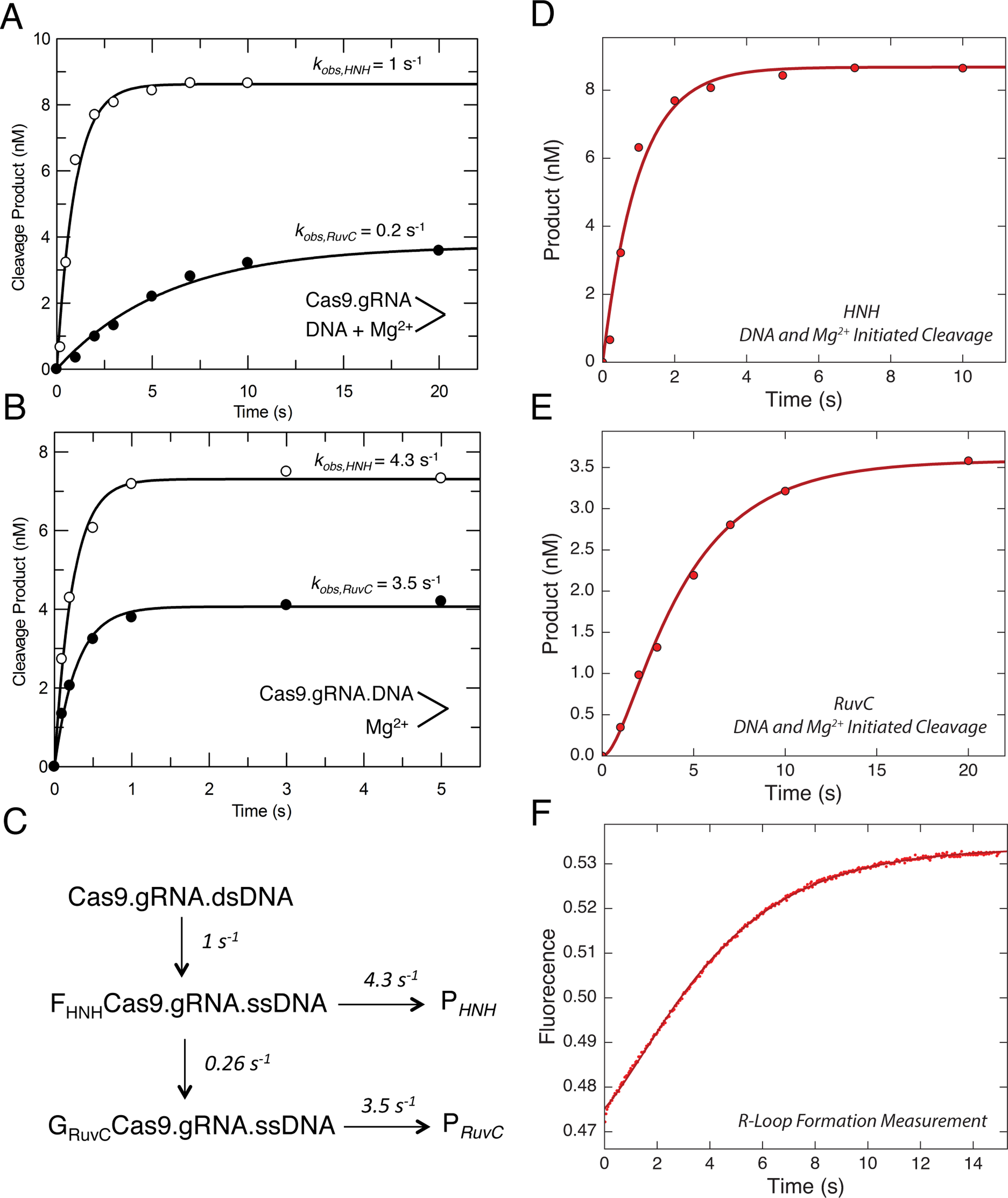
(A) Cas9 cleavage rates were measured after the reaction was initiated by the simultaneous addition of DNA (10 nM) and Mg2+ (10 nM) to Cas9.gRNA (28 nM active site concentration).
The reaction was quenched by the addition of EDTA at different time points, and then the results were fit to a single exponential equation. DNA was either labeled on the target strand or the nontarget strand to obtain the cleavage rates from HNH (open symbols) and RuvC (closed symbols) nuclease activities, respectively.
(B) HNH and RuvC cleavage rates measured after initiating the reaction by the addition of Mg2+ (10 nm) to a mixture of Cas9.gRNA (28 nM) with DNA (10 nm) pre-incubated for 10 min. Aside from the order of mixing, the experiment was performed and analyzed as in A.
(C) Model showing the kinetics of two isomerization steps preceding HNH and RuvC cleavage. This model was derived in fitting Figure D, E and F simultaneously. The global fitting of all three experiments provides an accurate estimation for the rate constants for R loop formation and subsequent cleavage reactions.
(D) Time dependence of HNH cleavage measured as in A. (E) Time dependence of RuvC cleavage, measured as in A. (F) R-loop formation was measured by mixing Cas9.gRNA (500 nM) with DNA with a 2AP label at position −9 on the non-target strand (100 nM) using stopped flow fluorescence method (Auto SF 120x, KinTek Corporation, Austin, TX.). The fluorescence increase as a function of time was biphasic defining two steps in R loop formation. The experiments including cleavage initiated by the simultaneous addition of DNA and Mg2+ for both HNH and RuvC cleavage were globally fit with the R loop formation measurement using the model shown in C.
