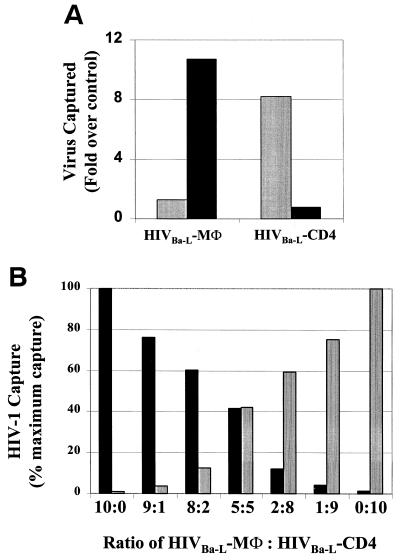
FIG. 2.
(A) Comparison of viral capture of macrophage- and lymphocyte-derived HIV-1. The HIV-1Ba-L-MΦ isolate was selectively captured by anti-CD36 (■). When HIV-1Ba-L-MΦ was propagated in T lymphocytes, the virus obtained (HIV-1Ba-L-CD4) was selectively captured by anti-CD26 ( ) and not by anti-CD36, indicating a discriminating phenotype for identifying the cellular origin of viral replication. (B) HIV-1Ba-L-MΦ and HIV-1Ba-L-CD4 isolates were mixed at various ratios and then captured with both anti-CD36 (■) and anti-CD26 (
) and not by anti-CD36, indicating a discriminating phenotype for identifying the cellular origin of viral replication. (B) HIV-1Ba-L-MΦ and HIV-1Ba-L-CD4 isolates were mixed at various ratios and then captured with both anti-CD36 (■) and anti-CD26 ( ). The amount of virus captured by each antibody was proportional to the input of each type of virus, further illustrating the selective capture of virus derived from diverse cell types. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
). The amount of virus captured by each antibody was proportional to the input of each type of virus, further illustrating the selective capture of virus derived from diverse cell types. Data are representative of three independent experiments.