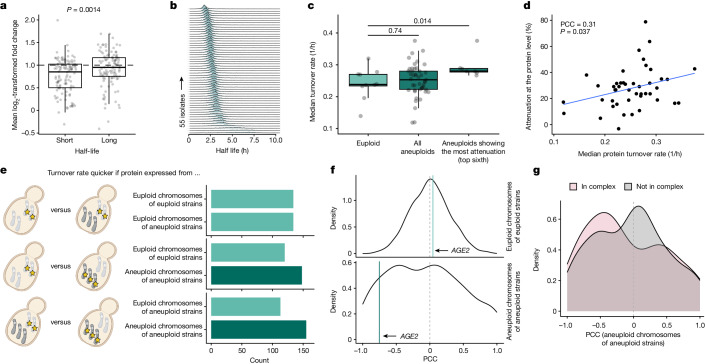
Fig. 5. Increased protein turnover in natural isolates is linked to dosage compensation.
a, Changes in protein abundance after inadvertent chromosomal duplications in aneuploid strains of the yeast deletion collection45 for proteins with short and long half-lives. Fold changes are defined as ratios between protein abundances and the median abundances of the respective protein across all strains. Long and short half-lives are defined as being >75% and <25% quantile (n = 110), respectively. P values were obtained by two-sided t-test. b, Stacked distributions of protein half-lives calculated for 55 isolates. c, Comparison of median turnover rates in euploid isolates (n = 10) versus all aneuploid isolates (n = 45) or isolates exhibiting high attenuation (n = 7). P values were determined using two-sample, two-sided Wilcoxon tests. d, Correlation between median turnover rate and protein-level dosage compensation in aneuploid isolates. Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC), P value and linear regression (blue line) are shown. The PCC and P value of the shown correlation do not change when genes expressed on aneuploid chromosomes in aneuploid isolates are excluded (PCC = 0.31, P = 0.037, two-sided). e, Comparison of median quantile-normalized turnover rates when a protein is expressed from aneuploid chromosomes, euploid chromosomes of aneuploid strains or euploid chromosomes of euploid strains. f, Distribution of PCCs between relative protein expression and isolate turnover rate determined for proteins expressed from euploid chromosomes of euploid isolates or aneuploid chromosomes. g, Distribution of PCCs for proteins expressed from aneuploid chromosomes split by protein-complex membership. In box plots, the centre marks the median, hinges mark the 25th and 75th percentiles and whiskers show all values that, at maximum, fall within 1.5 times the interquartile range.