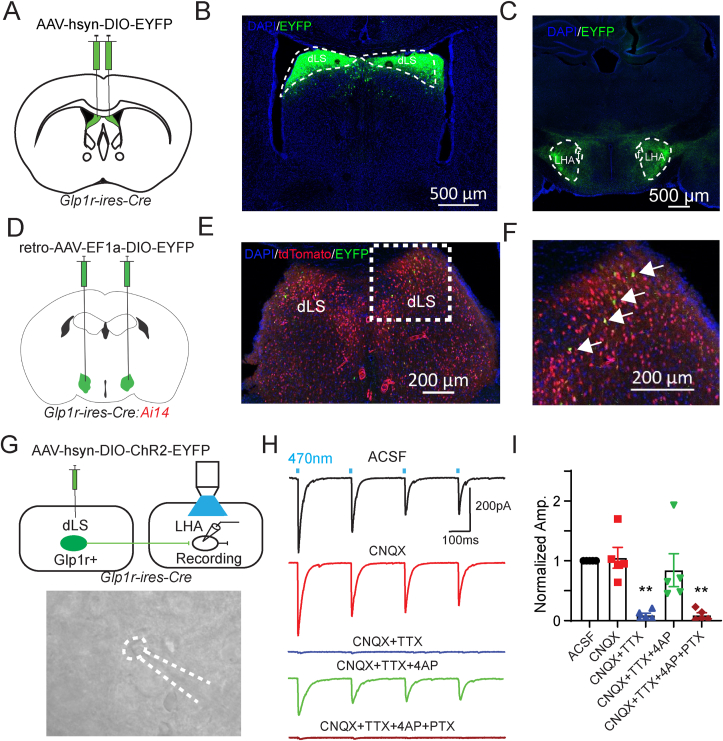
Figure 3.
dLSGLP−1Rneurons project to LHA.
(A) Glp1r-ires-Cre mice were injected in dLS with pAAV-hSyn-DIO-EYFP bilaterally.
(B and C) Viral-mediated expression of EYFP in dLSGLP−1R neurons soma (B) and axonal projections in the LHA (C) in Glp1r-ires-Cre mice.
(D) Glp1r-ires-Cre:Ai14 mice were injected in LHA with retro-pAAV-Ef1a-DIO-EYFP bilaterally.
(E and F) Images of coronal brain sections containing the dLS. White arrows indicate GLP-1R+/EYFP+ neurons.
(G) Schematic of experiment used to record postsynaptic currents in LHA neurons induced by optogenetic stimulation of dLSGLP−1R neurons. Glp1r-ires-Cre mice were injected in dLS with pAAV-EF1a-double floxed-hChR2(H134R)-EYFP-WPRE-HGHpA bilaterally and LHA neurons were patched.
(H) Representative trace of photostimulation (470 nm LED)-evoked IPSC in LHA neurons, which can be blocked by picrotoxin but not CNQX.
(I) Normalized IPSC amplitude before and after CNQX, TTX, 4AP and PTX application (one-way ANOVA, F(4,20) = 10.7, p < 0.0001, ∗∗Sidak's multiple comparisons test p < 0.01 vs. ACSF). n = 5 cells from 3 mice.
Data are presented as mean ± SEM.