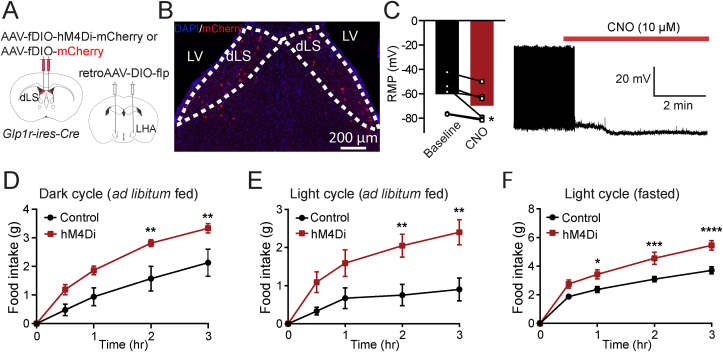
Figure 4.
dLSGLP−1R → LHA inhibition increases feeding.
(A) Brain schematic of viral injection for dLSGLP−1R → LHA neuron inhibition.
(B) Transduction of dLSGLP−1R → LHA neurons with hM4Di-mCherry.
(C) CNO application hyperpolarized the resting membrane potential and reduced the firing rate of dLSGLP−1R → LHA projection neurons (paired t-test, t(6) = 2.897, p = 0.0339, n = 6 cells from 3 mice).
(D–F) Chemogenetic inhibition of dLSGLP−1R → LHA projection neurons increased food intake (D) during the dark cycle when fed (two-way ANOVA, main effect of Group: F(1,40) = 26.01, p < 0.0001; main effect of Time: F(4,40) = 36.65, p < 0.0001, no interaction between Group and Time: F(4,40) = 1.993, p = 0.1142), (E) during the light cycle when fed (two-way ANOVA, main effect of Group: F(1,60) = 27.88, p < 0.0001; main effect of Time: F(4,60) = 11.68, p < 0.0001, no interaction between Group and Time: F(4,60) = 2.344, p = 0.0649), and (F) refeeding following an overnight fast (two-way ANOVA, main effect of Group: F(1,55) = 44.88, p < 0.0001; main effect of Time: F(4,55) = 104, p < 0.0001, interaction between Group and Time: F(4,55) = 3.795, p = 0.00085). n = 7 control an d6 hM4Di mice. Sidak's multiple comparisons test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
Data are presented as mean ± SEM.