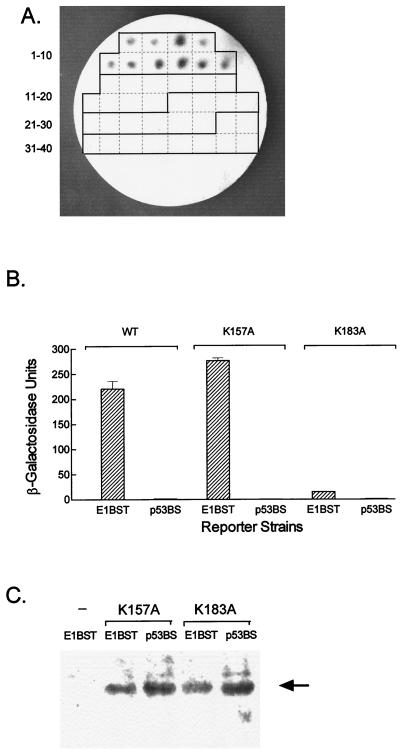
FIG. 5.
In vivo activity of E1DBD mutants. (A) The E1 K157A and K183A mutations were constructed in the AD-E1DBD background and transfected into both the E1BST-LACZ and p53BS-LACZ reporter strains. Ten transformants from each transfection were picked onto a grid plate (1-10, E1DBDK157A/E1BST-LACZ; 11-20, E1DBDK157A/p53BS-LACZ; 21-30, E1DBDK183A/E1BST-LACZ; 31-40, E1DBDK183A/p53BS-LACZ) and assayed for β-galactosidase activity as in Fig. 4. β-Galactosidase-positive, blue colonies (1-10) appear dark in this photo, while the negative, white colonies (11-40) are not visible. (B) Quantitative β-galactosidase assay for representative transformants from panel A. The reporter strains, E1BST-LACZ (designated E1BST) and p53BS-LACZ (designated p53BS), expressing either AD-E1DBDK175A (K157A bars), AD-E1DBDK183A (K183A bars), or the WT AD-E1DBD fusion (WT bars) were grown in liquid medium and assayed for β-galactosidase activity as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Western blot of the mutant transformants used in panel B. Cell extracts were prepared, electrophoresed on an SDS–10% polyacrylamide gel, transferred, and probed with an anti-AD serum. Lane 1 is a control extract from the E1BST-LACZ strain without an AD expression vector; lanes 2 to 5 are the four transformants of the two reporter strains with the E1DBD K157A or K183A mutations as indicated. The arrow marks the AD-E1DBD fusion protein.