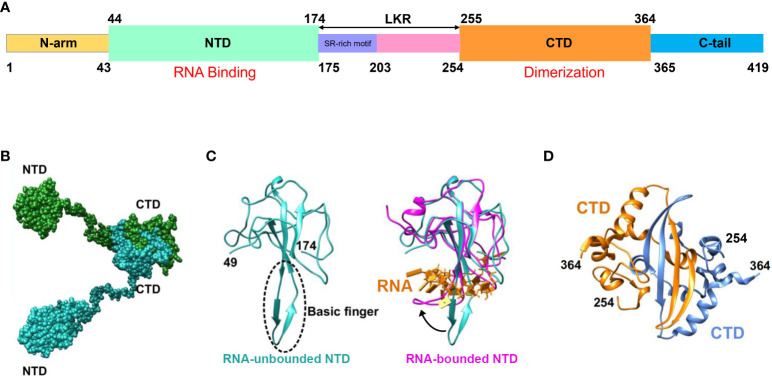
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of SARS-CoV-2 N protein structure. (A) Schematic depiction of the N-protein domains. Within the NTD, basic structural motifs are present that facilitate binding to viral genomic RNA, resulting in RNP formation. CTD comprises complementary motifs that promote N-protein dimerization. (B) Schematic illustration of the N protein structure following dimer formation. (C) Schematic diagram illustrating NTD crystal structure analysis. The blue region on the left represents the resolved NTD crystal structure in the absence of RNA binding (PDB ID: 6M3M), while the area enclosed by the dashed line denotes the basic amino acid motif involved in RNA affinity. The purple segment on the right indicates the resolved NTD crystal structure post-RNA binding (PDB ID: 7ACT), whereas the yellow portion signifies the bound RNA. The black arrow denotes the three-dimensional structural alteration of the NTD basic amino acid motif following RNA binding. (D) Analysis of the crystal structure of CTD yielding dimer formation (PDB ID: 6WZO) (Matsuo, 2021).