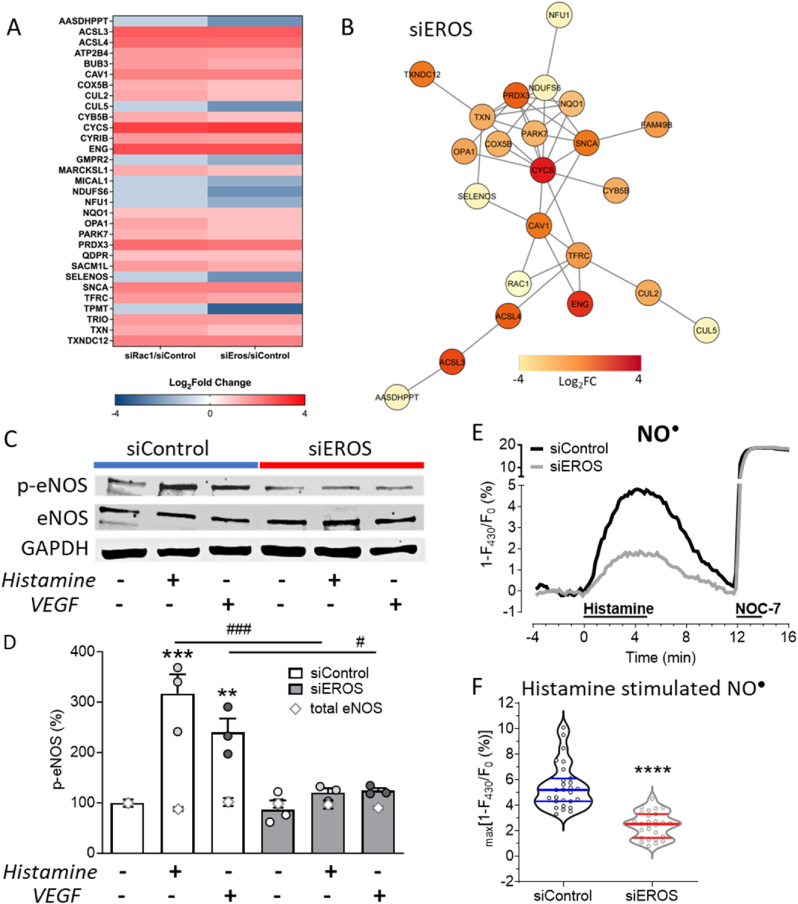
Fig. 5.
EROS knockdown induces reductive stress associated protein regulation resulting in diminished nitric oxide formation
A. Heat map of critical siEROS and siRAC1 regulated shared proteins identified in functional analysis. B. Network analysis shows most significant protein interactions. The network has been refined with a highest confidence cut off of 0.900. Nodes are colored based on calculated fold change. C. Representative immunoblots show abundances of eNOS phosphorylation (p-eNOS, Ser1177), total eNOS (eNOS) and GAPDH following transfection with Control or EROS siRNA in HUVEC after stimulation with histamine or VEGF vs. untreated. D. Analysis of p-eNOS blots reveals p-eNOS Ser1177 phosphorylation in siControl HUVEC stimulated with histamine or VEGF for 10 min, which is blocked in EROS downregulated HUVEC. Total eNOS (gray open rhombic characters) is unchanged among samples. All values are presented as mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared to untreated Control siRNA and #P < 0.05 or ###P < 0.001 compared to same treatments, either histamine or VEGF, of siEROS vs. siControl cells using 1way ANOVA. E. Average curves of NO● imaging experiments in Control (black curve) and EROS (gray curve) siRNA-transfected cells stimulated with histamine and NOC-7 as indicated. F. Statistical analysis of Control (n = 27) and EROS siRNA-transfected (n = 27) cells indicates decreased NO● levels following siRNA-mediated EROS knockdown, ****P < 0.0001 using unpaired t-test.