Figure 1.
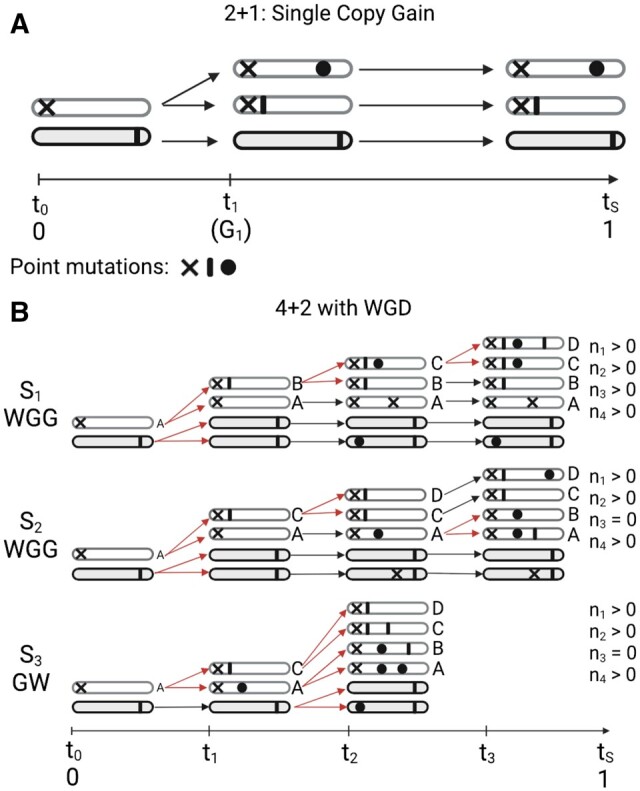
Principle behind timing amplifications. (A) A schematic representation of a single copy gain. Symbols represent point mutations occurring both before and after the depicted chromosomal gain. represents tumour initiation, or represents the time of the first gain, and represents the time of tumour sampling. Mutations occurring before are duplicated, and thus present on two chromosome copies. Mutations occurring after , or on the unaffected chromosome, are present on one chromosome copy. (B) A schematic representations of three scenarios (, , and ) leading to a copy number state of in a whole genome duplicated sample. W and G are used to refer to whole genome duplication (WGD) and gain, respectively. In a WGD event is followed by two sequential gains of the same chromosome, in which case mutations are expected to occur in all multiplicity states in the set . However, if no mutations of multiplicity three are observed, this suggests that the order of events may be a single gain followed by a whole genome duplication (), which can be timed, or a whole genome duplication followed by gains of two separate chromosomes (), which cannot be timed. Red lines indicate gain or WGD events. Image created with BioRender.com.
