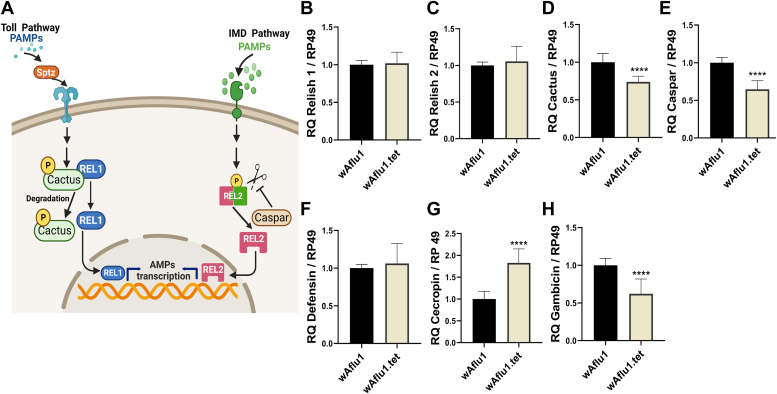
Figure 2.
Transcription of immune genes is modulated by Wolbachia in Ae. fluviatilis embryonic cell line.A, schematic representation (created with BioRender.com) summarizing the Toll and Imd immune pathways. When the Toll pathway is activated, it triggers signaling through adapter proteins that result in the phosphorylation and degradation of Cactus, a negative regulator that binds to the transcription factor Relish1 (REL1) in the cytoplasm. Cactus degradation allows REL1 translocation to the nucleus. When the Imd pathway is activated, the transcription factor Relish2 (REL2) is phosphorylated and cleaved by DREDD. DREDD activity is negatively regulated by Caspar. Activated REL2 translocates to the nucleus. Once inside the nucleus, both transcription factors can activate antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) transcription. B–H, REL1 (B), REL2 (C), Cactus (D), Caspar (E), defensin (F), cecropin (G), and gambicin (H) transcript fragments were amplified by RT-qPCR using cDNA from cells with or without Wolbachia (wAflu1 and wAflu1.tet, respectively). mRNA levels are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). RT-qPCR results were analyzed by t test; asterisks indicate significant differences (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). Imd, immunodeficiency; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns.