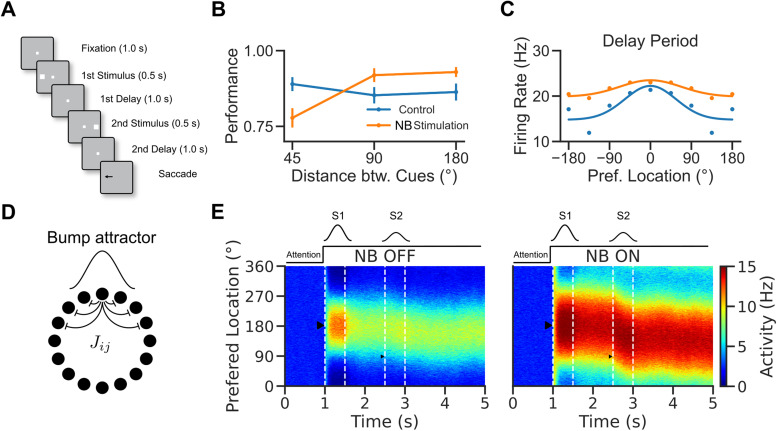
Figure 1.
A rate model to reconcile cholinergic modulation of behavior and neural tuning in a visuospatial WM task task. A, Visuospatial WM task with distraction (Qi et al., 2021). B, Performance of the monkeys in control and NB-stimulated trials. Performance was measured as percent of trials with responses within 7° visual angle of the target stimulus. C, Average prefrontal neuron location selectivity in the delay period (adapted from Qi et al., 2021). Blue: control trials. Orange: NB-stimulated trials. Dots: data. Lines: fits. D, Network scheme. The network consists of a population of 1,000 rate units with tuned connections. E, Activity versus neurons versus time, left: NB OFF condition, right: NB ON condition ( simulates increased excitability induced by NB stimulation). After 1 s in baseline activity, neurons receive a tuned stimulus, S1, and a nonspecific attention signal is switched on. The activity becomes structured into a bump. The bump is only slightly perturbed by a second weak stimulus, S2, so the bump maintains a location around S1. Triangles show the locations of the stimuli.