Figure 6.
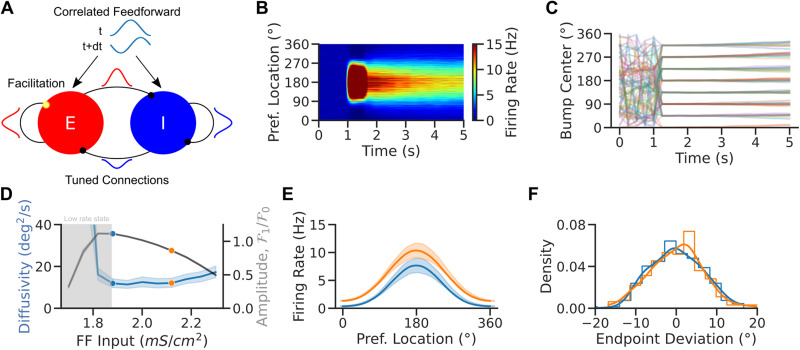
Enhanced excitability weakens network tuning but weakly impacts bump diffusion in spiking attractor networks. A, Network scheme. Spiking EI network with tuned connections (ring model) and facilitating E-to-E synapses. Neurons receive a weakly tuned FF input with a random phase at each time step to induce spatial correlations. B, Local average firing rate versus time versus preferred location for one trial in the NB OFF condition. C, Population activity center of mass in 30 simulations for eight different cue locations. D, Diffusivity (blue) and tuning amplitude (black) versus FF input at time t = 5 s in the simulations of panel C (averaged over 8 cues and 60 random initializations per cue). E, Population tuning curves averaged over trials at the end of the delay period (tuning curves were recentered before averaging). Increased excitability leads to weaker tuning in the NB ON condition. F, Endpoint deviations (mean corrected endpoint). Colors match dots in D. Lines are kernel density estimates. Error bands 95% confidence intervals.