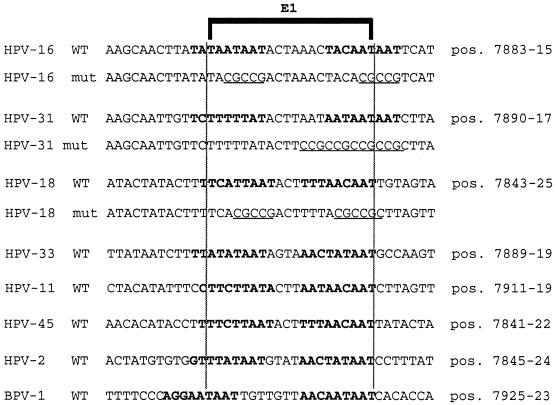
FIG. 2.
Alignments of presumed and known binding sites for the replication factor E1 in seven genital HPV types and in BPV-1 coincide with binding sites for the transcriptional repressor PSM-BP (or CDP/Cut, respectively). The alignment of E1 binding sites was done as in a study by Holt and Wilson (26) extended by a sequence comparison (44). A bracket indicates the presumed E1 consensus binding sequence. Bold letters identify the PSM of HPV-16 and similarities in six other HPV types. Since CDP/Cut binding sites do not show a strict consensus sequence, with multiple 5′-TAAT-3′ 5′-CAAT-3′ motifs at variable positions and orientations being the hallmark of the generally AT-rich sequences, the identification of CDP/Cut targets in these PSMs is conjectural. The mutations (underlined) were aimed at eliminating all of the 5′-TAAT-3′ and most of the 5′-CAAT-3′ elements. All of these sequences overlap with the position 1 of the circular genomic map. The exact genomic position is shown on the right. The sequences shown represent oligonucleotides that were examined by EMSA and cloned in the form of BamHI-BglII fragments into the CAT expression vector p80SV for functional tests. Oligonucleotides that were inserted in the sense orientation in this vector were identified by DNA sequencing.