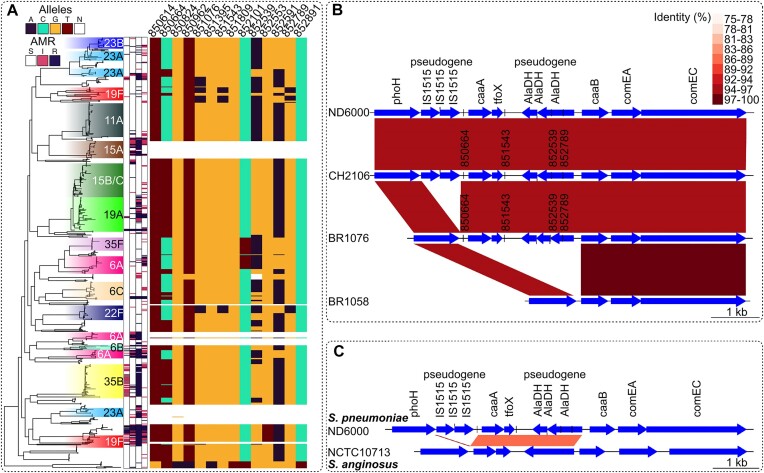
Figure 3.
Overview of genomic variations of the flanking region of the TfoX competence regulator demonstrated using the Massachusetts S. pneumoniae dataset. (A) The phylogenetic tree (n = 616) is coloured according to the serotype shown to the right of the tree. The 4 bars immediately to the right denote the antimicrobial resistance data for ceftriaxone, erythromycin, benzyl penicillin and trimethoprim, respectively. The key above indicates the colour shadings for S – sensitive, I – intermediate and R – resistant. Allelic variation in the tfoX locus is shown by the rightmost heatmap and the key above shows the colour for each nucleotide with N indicating an ambiguous base. SNP positions above the heatmap are based on the ATCC 700669 reference. This suggests that the tfoX locus is present in most pneumococci and can be divided into three genotypes: that containing the major alleles at each polymorphic site; that containing the minor alleles at sites 850664 and 852539, and that containing the minor alleles at these two sites, as well as sites 851543 and 852789. (B) The alignment of representatives of the four observed genotypes in the dataset, demonstrated here using sample data from selected isolates. Colour shading indicates the identity between regions. In ND6000 (ERR129187) and CH2106 (ERR129095), the flanking region is intact with multiple insertion sequences, two functional genes, a non-coding region and an alaDH pseudogene. The locus is intact, but the insertion sequences are not observed in BR1076 (ERR129048). In contrast, the entire locus is missing in BR1058 (ERR129043). With reference to the phylogenetic tree in (A): ND6000 is a serotype 7C isolate between regions 19F and 11A, CH2106 is a 19F isolate, BR1076 is 6C isolate and BR1058 is a 7C isolate. (C) Shows the alignment between FM211187 and S. anginosus NCTC10713 genomes. For the region of interest, this is the most similar locus among streptococcal species. Despite the general divergence between S. pneumoniae and S. anginosus, the tfoX-alaDH gene pair is intact in both species with high similarity (same key as in (B) to show region identity). However, the dissimilarity between the flanking regions demonstrates the typical level of divergence between the genomes. Hence, the localized similarity indicates a possible recent introgression into the pneumococcus.