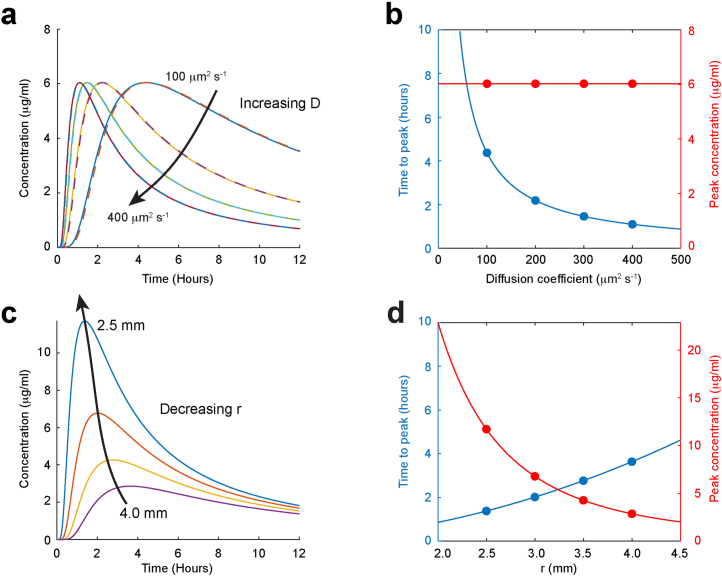
Extended Data Fig. 6. The time course of C(r, t).
a, b According to equation [2], the concentration at a fixed distance, r, from a Gaussian source (solid lines) reaches a peak with time that depends only on the diffusion coefficient D, while the peak concentration does not change. Almost identical concentrations are predicted if the source is a sphere, rather than a Gaussian, containing the same number of moles (dashed lines). (The equation for the concentration as a function of time from a spherical source has been solved by Crank26.) c,d, The peak concentration with time for a fixed diffusion coefficient, decreases with increasing distance r, with relatively small changes in the time to peak.