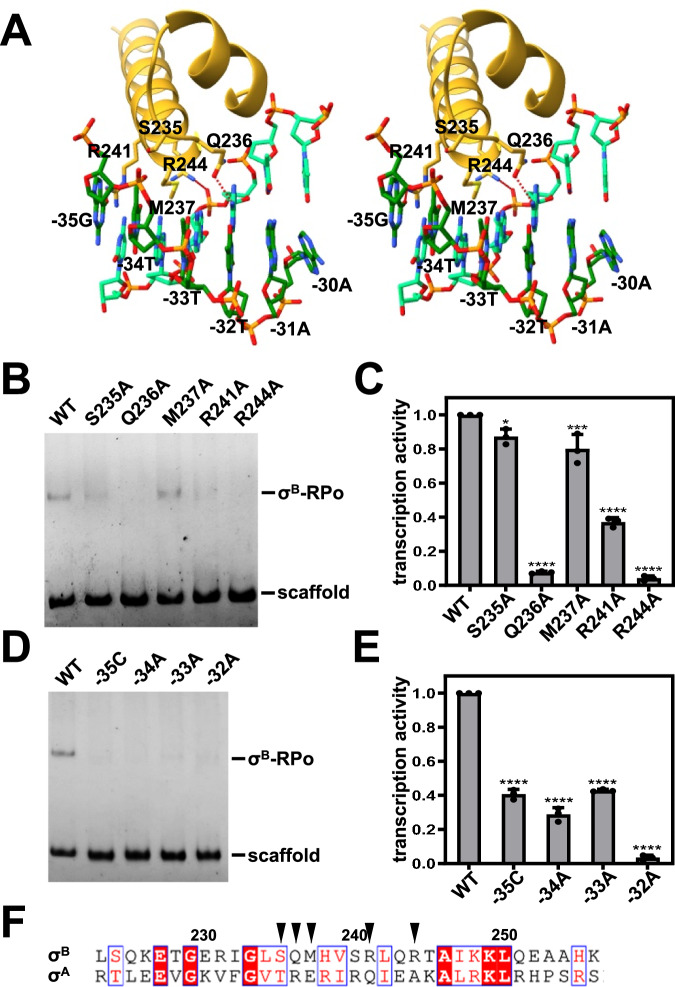
Fig. 2. σ-DNA interactions responsible for −35 element recognition.
A σB4-DNA interactions are depicted in stereo view. Yellow, σB4; dark green, nontemplate strand DNA; light green, template strand DNA. The potential hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. B EMSA shows that the substitution of DNA interacting residues impairs σB-RPo formation. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. C Ribogreen transcription assay shows that the substitution of DNA interacting residues impairs σB dependent transcription. Error bars represent mean ± SD of n = 3 experiments. S235A, p = 0.0252; Q236A, p < 0.0001; M237A, p = 0.0008; R241A, p < 0.0001; R244A, p < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. D EMSA shows that the mutation of the interacting nucleotides impairs σB-RPo formation. E Ribogreen transcription assay shows that the mutation of the interacting nucleotides impairs σB dependent transcription. Error bars represent mean ± SD of n = 3 experiments. −35C, p < 0.0001; −34A, p < 0.0001; −33A, p < 0.0001; −32A, p < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. F Sequence alignment of S. aureus σA and σB. The DNA interacting residues of σB are indicated by black triangles. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.