Figure 2.
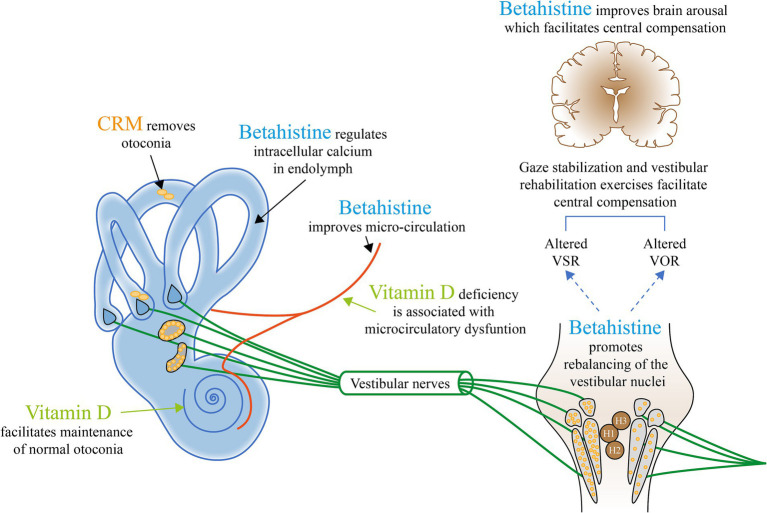
The current potential management approaches that may be considered based on known and proposed mechanisms of BPPV. H, Histamine; VOR, Vestibular ocular reflex; and VSR, Vestibulospinal reflex. Appropriate canalith repositioning maneuvers (CRMs) to remove the otolith from the semicircular canal provide relief from symptoms and positional nystagmus in up to 92% with ≥1 CRMs (36). Vitamin D deficiency is associated with microcirculatory dysfunction (59, 118). The biologically active form of vitamin D is involved in the upregulation of epithelial Ca2+ channel transporters that helps maintain low endolymph Ca2+, retain the capacity to dissolve exfoliated otoconia, and prevent abnormal otoconia (55).† Betahistine increases local vestibular blood flow (56)† and is involved in the regulation of intracellular calcium, which helps to reduce/delay otoconial detachment (51).† Betahistine also facilitates central vestibular compensation by enhancing the rebalancing of the neuronal activity of the vestibular nuclei complexes on both sides (50, 64)† and (67).‡ Betahistine also improves brain arousal, a crucial factor for functional recovery/behavioral adaptation, through general upregulation of histamine (15, 50, 58).† Gaze stabilization and vestibular rehabilitation exercises facilitate central compensation and reduce symptoms of dizziness and vertigo (1, 61).‡ †Evidence from animal studies. ‡Evidence from clinical studies.