Figure 3.
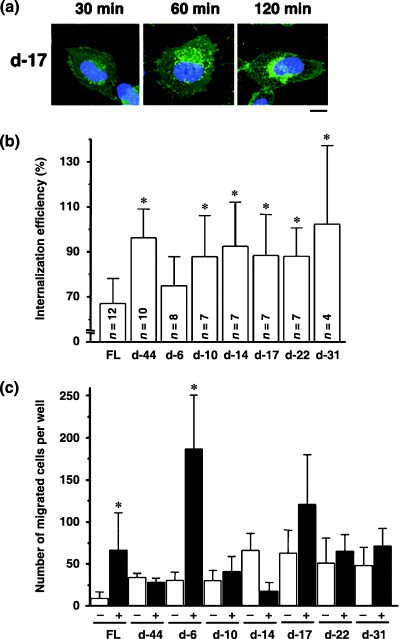
Identification of the amino acids required for steady‐state CXCR4 internalization. (a) Amino acid sequences of the cytoplasmic tail of FL and deletion mutants. Residues in red are required for ligand‐induced endocytosis. (b) The protein expression of each mutant in 293T cells was verified by Western blot analysis. (c) Confocal micrographs of NP2 cells expressing FL and d‐44 mutant proteins. The blue signal represents the Hoechst‐stained nucleus. (Original magnification, ×630; bar, 10 µm.) (d) Confocal micrographs showing NP2 cells expressing CXCR4 FL stained with ER, Golgi, or lysosome organella markers. The organella marker signal is shown in red, the GFP signal is in green. The pixels that both red and green signals co‐localized are shown in yellow. (Original magnification, ×630; bar, 10 µm.) (e) CXCR4 FL trafficking in the absence of SDF‐1α in NP2 cells. Cell surface CXCR4 FL was labeled with an antibody conjugated with PE‐Cy5 (red), incubated at 37°C for the indicated times, fixed and imaged. (Original magnification, ×630; bar, 10 µm.) (f) Confocal micrographs of NP2 cells expressing FL and mutant proteins. The intracellular vesicular green fluorescence reflecting steady‐state internalization can be seen in the d‐6 mutant. The blue signal represents the Hoechst‐stained nucleus. (Original magnification, ×630; bar, 10 µm.)
