Figure 3.
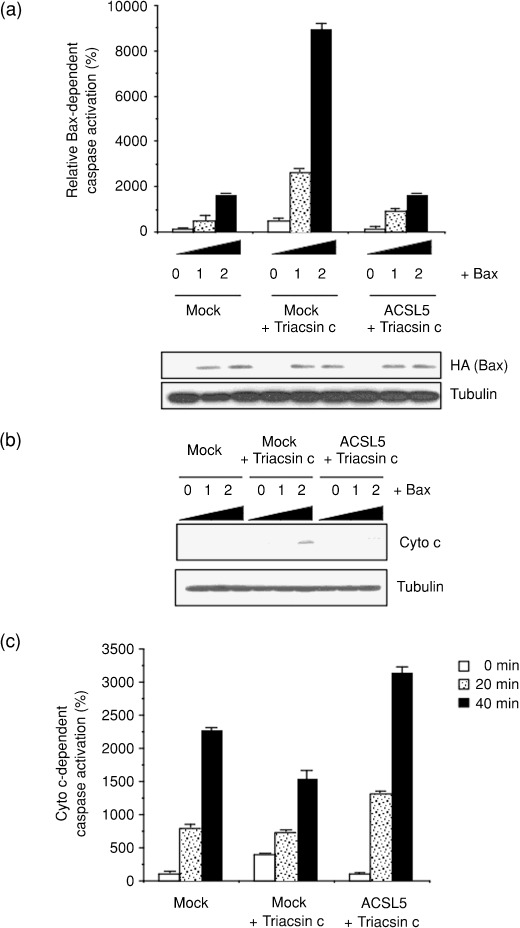
Potentiating the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by acyl‐CoA synthetase (ACS) inhibition. (a) To estimate Bax‐induced caspase activation, mock‐ and ACSL5‐transduced SF268 cells were seeded in six‐well plates and transiently transfected with pCGBL‐HA‐Bax (0, 0.1, and 0.2 µg/well) and pGVC, a luciferase‐expressing construct (0.4 µg/well). At 6 h after transfection, cells were left untreated or were treated with 1 µM Triacsin c for an additional 24 h. Each cell lysate was prepared and caspase activity measured as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. The expression of Bax (HA) was examined by western blot. The expression of α‐tubulin was analyzed as a loading control. (b) Cells were transiently transfected with the Bax plasmid vector and then were treated with Triacsin c as in (a). Cytochrome c release from the mitochondria to cytoplasm was monitored by western blot analysis. (c) Mock‐ and ACSL5‐transduced SF268 cells were left untreated or treated with 1 µM Triacsin c for 24 h. Cytosolic extracts were prepared and incubated with 10 µM cytochrome c and 1 mM dATP for 0–40 min. After the incubation, caspase activity was measured, as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. In (a) and (c), data are mean values of three independent experiments. Error bars show standard deviations.
