Figure 2.
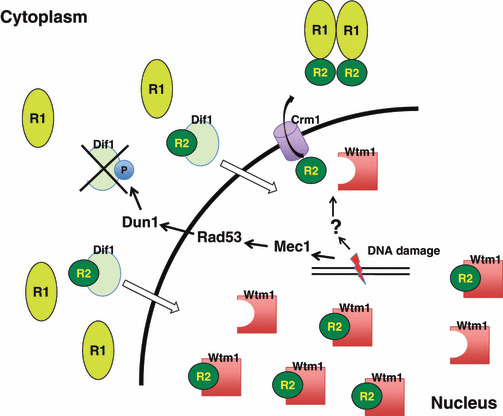
Regulation of subcellular localization of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) in budding yeast. The small subunit Rnr2‐Rnr4 (R2) localizes at the nucleus, whereas the large subunit Rnr1 (R1) is cytoplasmic outside of S phase. After DNA damage or during S phase, the Rnr2‐Rnr4 subunit enters the cytoplasm enabling it to bind to Rnr1, forming an active complex. Dif1 directly binds to the R2 complex which promotes the import of R2 into the nucleus. The imported R2 then forms a complex with Wtm1, which anchors the complex in the nucleus. In the presence of DNA damage, the association of R2 with Wtm1 is disrupted. Furthermore, DNA damage‐induced activation of the Mec1‐Rad53‐Dun1 axis directly phosphorylates (P) Dif1, which inactivates and triggers its degradation. A reduction in Dif1, together with the dissociation of R2 from Wtm1 after DNA damage, allows R2 to enter the cytoplasm.
