Figure 1.
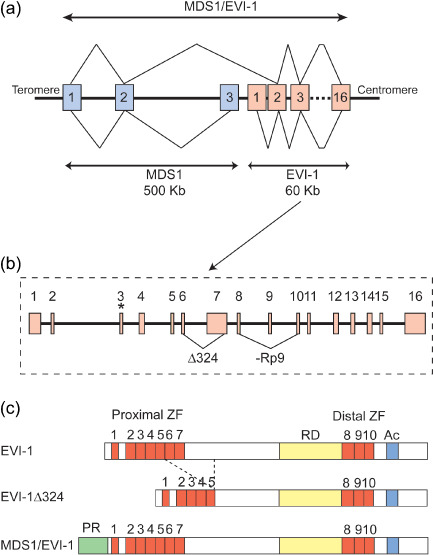
Structure of ecotropic viral integration site‐1 (EVI‐1) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) 1–EVI‐1. (a) Genomic structure of human EVI‐1, MDS1, and MDS1–EVI‐1. Exons are represented by boxes and numbered. Z‐lines represent splicing to produce mRNA. The MDS1 gene has three exons and spans 500 kb. The EVI‐1 gene spans only 60 kb but has 16 exons. MDS1–EVI‐1 is produced by splicing of the second exon of MDS1 and the second exon of EVI‐1. (b) Detailed genomic structure of human EVI‐1. The translation start codon of EVI‐1 in exon 3 is indicated by an asterisk. The alternative splice variants are indicated by triangular lines. (c) Diagrams of EVI‐1, EVI‐1Δ324, and MDS1–EVI‐1 proteins. EVI‐1 has two sets of the zinc finger domains (ZF). Between the two sets of zinc finger domains, a repression domain (RD) has been identified as well as an acidic region (Ac) at the C‐terminus. Structurally in MDS1–EVI‐1, the PR domain is located at the N‐terminus of EVI‐1. Another naturally occurring splice variant, EVI‐1Δ324, has been described that lacks 324 internal amino acids including zinc fingers 6 and 7 of the proximal zinc finger domain.
