Figure 2.
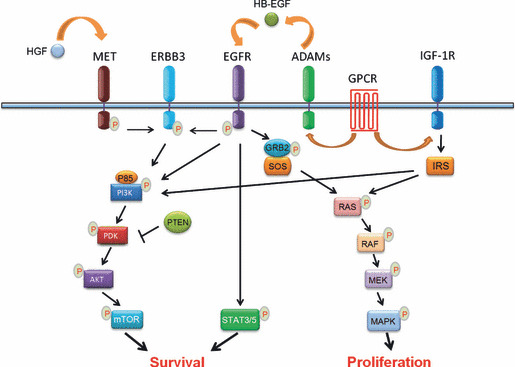
Simplified schematic illustration of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling network. After ligand stimulation, EGFR is activated and directly transmits signals to downstream pathways, including the phosphatidylinositol‐3‐kinase (PI3K)/3‐phosphoinositide‐dependent protein kinase (PDK)/v‐akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3/5 (STAT3/5) pathways for cell survival, and the rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (RAS)/v‐raf‐1 murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog (RAF)/MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK)/MAPK pathway for cell proliferation. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) inhibits AKT activity through PDK. The EGFR pathway cross‐talks with other signaling pathways: either hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) activation by hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulation or EGFR activation is able to transmit signals through erythroblastic leukemia viral (v‐erb‐b) oncogene homolog 3 (ERBB3) and results in the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway; and G‐protein coupled receptor (GPCR) activation enhances EGFR signaling through a disintegrin and metalloproteinases (ADAMs) that shed pro‐heparin‐binding EGF‐like growth factor (HB‐EGF) and increase the amount of HB‐EGF. As well as the cross‐talk with GPCR signaling, insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor (IGF‐1R) signaling through insulin receptor substrate (IRS) activates the PI3K/PDK/AKT/mTOR and RAS/RAF/MEK/MAPK pathways, which are commonly shared by EGFR signaling. GRB2, growth factor receptor‐bound 2; P, phosphorylation; SOS, son of sevenless homolog; P85, phosphatidylinositol 3‐kinase regulatory subunit.
