Figure 1.
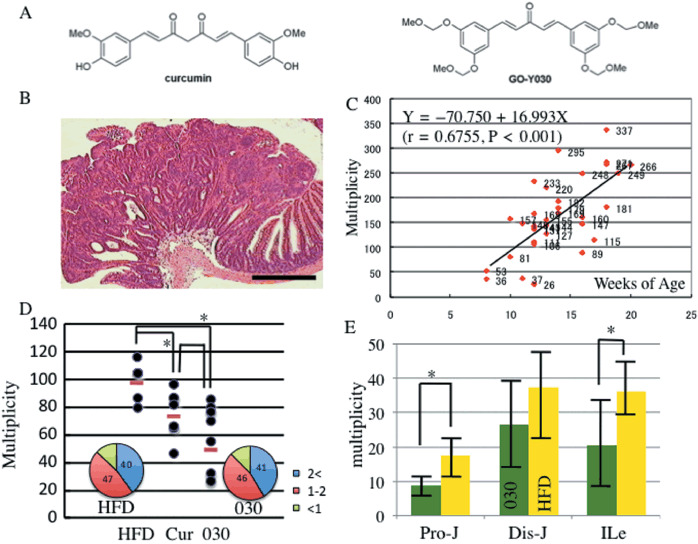
New curcumin analog and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) mouse model. (a) Chemical structures of curcumin and GO‐Y030 [(1E, 4E)‐1,5‐bis‐(3,5(‐bismethoxymethoxyphenyl)penta‐1,4‐dien‐3‐one]. (b) Histological appearance of intestinal tumor in Apc580D/+ mice. Scale bar = 400 µm. Histological features of these tumors correspond to those seen in adenomas. (c) Correlation between tumor incidence and aging of Apc580D/+ mice. Intestinal tumors are apparent at 8 weeks of age. The multiplicity reaches over 100 at around 12 weeks of age in almost all cases. Pearson's correlation coefficient (r) and linear regression equations were calculated. (d) Total tumor multiplicity in Apc580D/+ mice fed curcumin analogs. Apc580D/+ mice were fed the basal diet (HFD), curcumin (cur), or GO‐Y030. In the inset, the frequency of each tumor size: large (>2 mm diameter, blue), middle (1–2 mm, red), and small (<1 mm, green). *P < 0.05. (e) Multiplicity of adenomas in each intestinal segment in each diet group. Results are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05. Pro‐J, proximal jejunum; Dis‐J, distal jejunum; Ile, ileum.
