Figure 4.
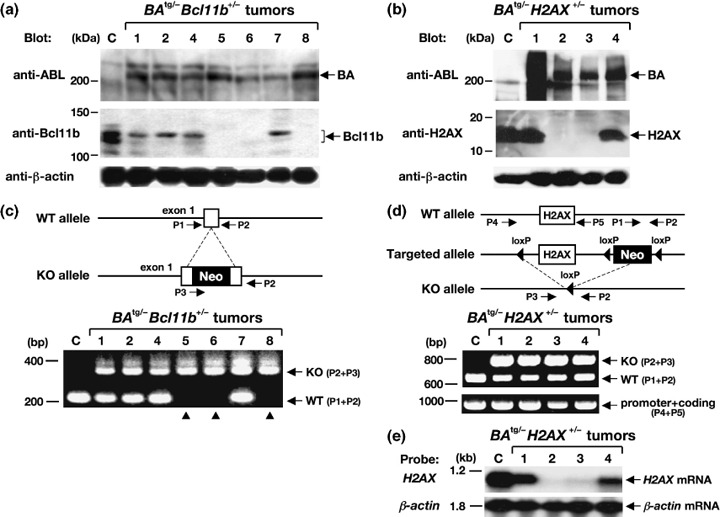
Gene expression and PCR analyses of the tumors that developed in BA tg/– Bcl11b +/– (left panels) and BA tg/– H2AX +/– (right panels) mice. (a,b) Western blot analysis for the expression of p210BCR/ABL, Bcl11b, and H2AX proteins. Proteins extracted from a control (C) thymus and tumor tissues of BA tg/– Bcl11b +/– (no. 1, 2, and 4–8) and BA tg/– H2AX +/– mice (no. 1–4) were blotted with an anti‐ABL antibody (upper panels) and anti‐Bcl11b or anti‐H2AX antibody (middle panels). The positions of p210BCR/ABL (BA), Bcl11b, and H2AX proteins are indicated by arrows. An anti‐β‐actin blot was carried out as an internal control (bottom panels). Protein markers are shown on the left. (c,d) Schematic illustrations of wild‐type and targeted alleles for Bcl11b and H2AX genes (upper panels) and the resultant genomic PCR products (lower panels). DNA extracted from a control (C) thymus and tumor tissues of BA tg/– Bcl11b +/– (no. 1, 2 and 4–8) and BA tg/– H2AX +/– mice (no. 1–4) were amplified with sets of primers (P1 and P2 for wild‐type [WT] alleles, P2 and P3 for knockout [KO] alleles, and P4 and P5 for a part of the promoter and the whole coding region of H2AX). The positions of primers are shown in the upper panels and WT‐ and KO‐derived PCR products are indicated by arrows in the lower panels. Molecular markers are shown on the left. Samples without Bcl11b expression are indicated by arrowheads. Neo, neomycin resistance gene. (e) Expression of H2AX mRNA in BA tg/– H2AX +/– tumors. RNA extracted from a control thymus (C) and tumor tissues of BA tg/– H2AX +/– mice (no. 1–4) were hybridized with H2AX cDNA probe. β‐Actin hybridization was carried out as an internal control. Molecular markers are shown on the left.
