Figure 1.
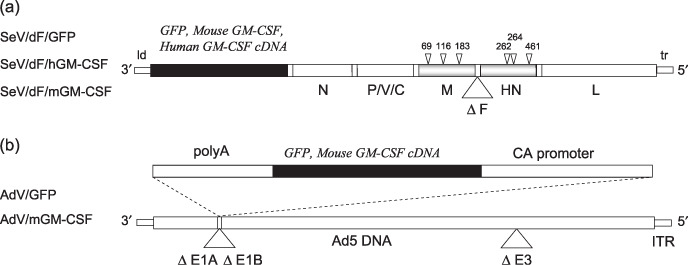
Schematic representation of the viral vectors used in the present study. (a) The three recombinant Sendai virus (SeV) vectors (SeV/dF/GFP, SeV/dF/mGM, and SeV/dF/hGM) were based on the Z‐strain of SeV. The SeV genome is delimited by two promoter regions: the leader (ld) and the trailer (tr) regions. The respective exogenous genes (green fluorescent protein [GFP], mouse granulocyte macrophage colony‐stimulating factor [GM‐CSF], and human GM‐CSF) were inserted between the ld and the open reading frame of the N gene. The SeV genes encode the envelope‐related proteins M, F, and HN, and the negative‐stranded genomic ribonucleotide‐protein complex (RNP) proteins N, P/V/C, and L. Temperature‐sensitive recombinant SeV/dF vectors lose expression of the envelope‐related M and HN genes, and have ribonucleotide substitutions in the M, HN, and L genes, as indicated by the arrowheads.( 23 ) (b) The recombinant adenovirus vectors containing the GFP or mouse GM‐CSF cDNA expression cassettes (AdV/GFP or AdV/mGM‐CSF) were constructed by homologous recombination between the expression cosmid cassette and the parental virus genome.( 24 ) The expression of these genes was driven by a CAG promoter. These replication‐defective adenovirus serotype 5 (Ad5)‐based vectors have deletions in the E1A, E1B, and E3 regions. ITR, internal terminal repeat.
