Figure 4.
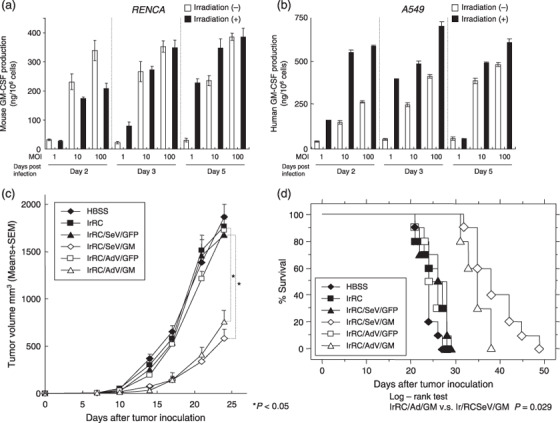
In vitro effects of irradiation on granulocyte macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) production from SeV/dF/G‐transduced tumor cells and in vivo effects of irradiated Sendai virus (SeV)‐ or adenovirus‐mediated GM‐CSF‐transduced RENCA vaccine cells against established tumors. (a,b) Levels of GM‐CSF produced from SeV/dF/mGM‐transduced mouse RENCA cells or SeV/dF/hGM‐transduced human H1299 cells with or without irradiation (on day 1) were measured comparatively at multiplicities of infection (MOI) of 1, 10, and 100 on days 2, 3, and 5 after transduction by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assays. (c) One million of the parental RENCA cells were inoculated subcutaneously into the right flank of BALB/c mice (n = 9), followed by subcutaneous inoculation of 1 × 106 cells of the indicated RENCA vaccine in the left flank weekly for three times (on days 7, 14, 21). The treatment groups included Hank's buffered salt solution (HBSS) only, irRC, irRC/AdV/GFP, irRC/AdV/GM, irRC/SeV/GFP, and irRC/SeV/GM cells. For adenovirus‐ or SeV‐mediated transduction for preparing tumor vaccine cells, RENCA cells were transduced with adenovirus or SeV at a MOI of 300 or 100, respectively. Tumor volume was monitored twice or three times per week. (d) Survival curve of the RENCA‐bearing mice treated with tumor vaccination as described above. Bar graphs depict the means ± SEM. Significant differences are denoted with asterisks (*P < 0.05).
