Figure 6.
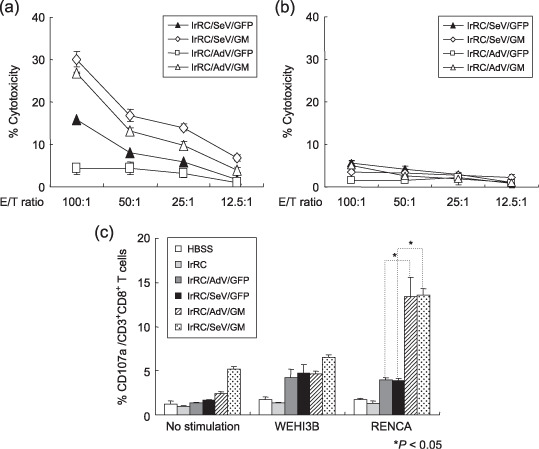
In vitro cytotoxicity assays and the effector cells contributing to the antitumor effects induced by the irradiated Sendai virus (SeV)‐ or adenovirus (AdV)‐mediated granulocyte macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF)‐transduced RENCA vaccine cells. (a,b) Seven days after the third tumor vaccination with irRC/AdV/GFP, irRC/SeV/GFP, irRC/AdV/GM, or irRC/SeV/GM cells, mice were killed to harvest splenocytes. Splenocytes were restimulated with mitomycin C‐treated RENCA cells for 6 days and used as effector cells in a 51Cr‐release assay. (a) 51Cr‐labeled RENCA cells used as target cells and (b) WEHI‐3B cells used as non‐specific target cells were cocultured with effector cells at the indicated effector to target (E : T) ratios for 5 h. (c) CD107a mobilization of splenic CD8+ T cells from mice treated with the indicated tumor vaccinations. Splenocytes were restimulated in vitro for 72 h with RENCA cells. The cells were then cultured with or without RENCA or WEHI‐3B cells for an additional 5–6 h. The percentages of CD107a‐expressing CD3+CD8+ T cells are indicated. The values represent the means ± SEM of the percentage cytotoxicity. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown.
