Figure 3.
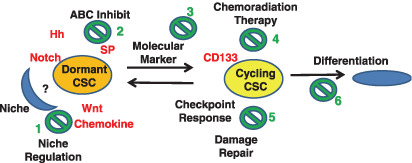
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) and chemoradiation therapy. In the schema, dormant CSCs are supported by a niche and resistant therapy, whereas cycling CSCs give rise to the volume of tumors and are sensitive to the genotoxic chemoradiation therapy. If so, the remaining CSCs followed by apparent chemoradiation therapy would contribute to the regrowth and metastasis of tumors. The possible therapeutic approaches include: (1) targeting niche regulation through inhibition of stem cell Hh, Notch, and Wnt signaling and chemokine, which inhibit CSCs through the interference of self‐renewal; (2) inhibition of ABC transporters such as SP; (3) targeting molecular markers such as CD33 and imatinib for tyrosine kinase bcr‐abl; (4) chemoradiation therapy; (5) control of checkpoints, such as inhibition of Chk1 and Chk2; and (6) induction of differentiation, such as retinoic acid.
