Figure 1.
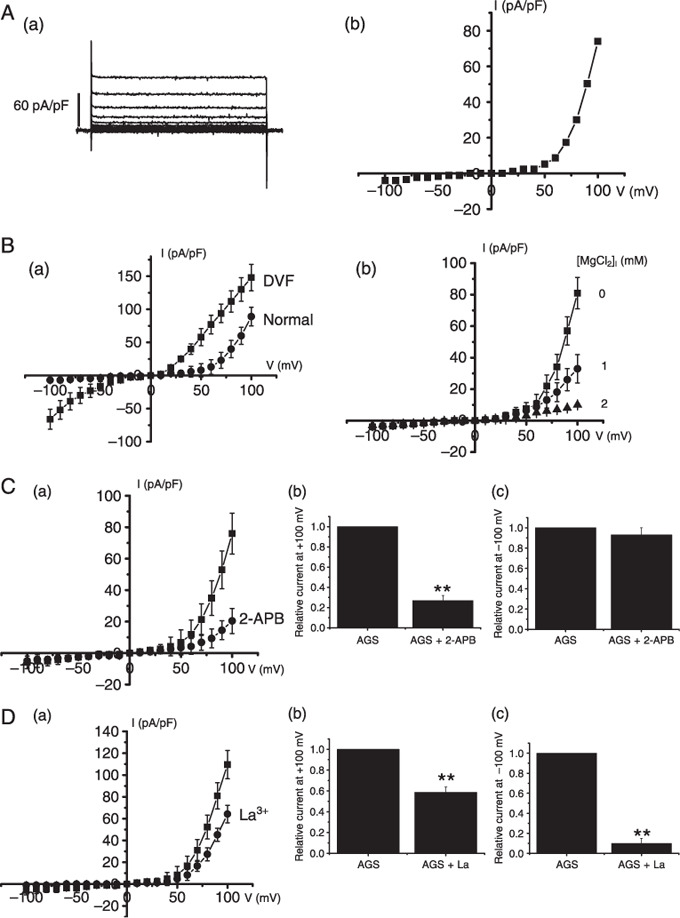
Electrophysiologic and pharmacologic characteristics of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7)–like current in AGS cells. (A‐a) From a holding potential of –60 mV, single steps of 100 ms duration were applied in 10 mV increments (–100 to +100 mV). An outward‐rectifying current slowly developed over time with peak current amplitudes occurring 5–8 min after obtaining the whole‐cell configuration. This current displayed no notable inactivation over the duration of the pulse. (A‐b) I–V curve from the same cell is shown. Results are from representative AGS cells. (B‐a) Representative TRPM7‐like currents in AGS cells. A voltage ramp from –100 to +100 mV was applied from a holding potential of –60 mV (normal,  ). The complete removal of external divalents increases both inward and outward monovalent current flow with little rectification (divalent free [DVF],
). The complete removal of external divalents increases both inward and outward monovalent current flow with little rectification (divalent free [DVF],  ). (B‐b) TRPM7‐like currents in AGS cells at 0, 1, or 2 mmol/L [Mg2+]i. A voltage ramp from –100 to +100 mV was applied from a holding potential of –60 mV. (C) Effect of 2‐APB on TRPM7‐like current. I–V curves and summary bar graph in the absence (
). (B‐b) TRPM7‐like currents in AGS cells at 0, 1, or 2 mmol/L [Mg2+]i. A voltage ramp from –100 to +100 mV was applied from a holding potential of –60 mV. (C) Effect of 2‐APB on TRPM7‐like current. I–V curves and summary bar graph in the absence ( ) and presence (
) and presence ( ) of 100‐µmol/L 2‐APB. (D) Effect of La3+ on TRPM7‐like current. I–V curves and summary bar graph in the absence (
) of 100‐µmol/L 2‐APB. (D) Effect of La3+ on TRPM7‐like current. I–V curves and summary bar graph in the absence ( ) and presence (
) and presence ( ) of 100‐µmol/L La3+. **P < 0.01.
) of 100‐µmol/L La3+. **P < 0.01.
