Figure 7.
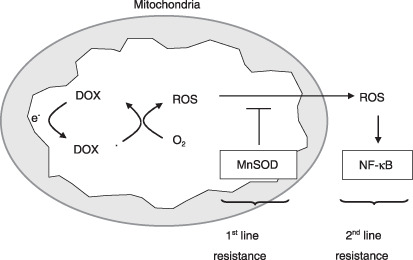
A hypothetical mechanism underlying doxorubicin (DOX) resistance in gastric cancer cells. Manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) first removes mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by DOX as the first‐line resistance, and then nuclear factor‐κB (NF‐κB) secondly enables cancer cells to survive under oxidative stress conditions as the second‐line resistance.
