Figure 2.
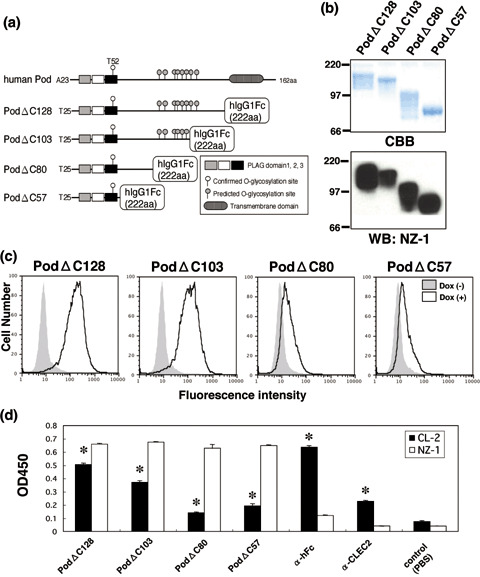
Binding activity of podoplanin–Fc chimeras to C‐type lectin‐like receptor‐2 (CLEC‐2). (a) Podoplanin–Fc deletion mutants were produced as shown in this scheme. (b) Purified podoplanin–Fc chimeras (10 or 0.1 µg/lane) were electrophoresed using 10–20% gels and either stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) or western blotted with NZ‐1. (c) Expression of CLEC‐2 was induced by the addition of 1 µg/mL doxycycline to 293T‐REx/CLEC‐2 cells 24 h before experimentation. Cells were harvested by brief exposure to 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. After washing with phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS), doxycycline+ or doxycycline− cells were treated with podoplanin–Fc chimeras for 1 h at 4°C followed by treatment with antihuman Fc (2 µg/mL) and Oregon green‐conjugated antirabbit IgG (2 µg/mL). Fluorescence data were collected using by flow cytometry. (d) Podoplanin–Fc chimeras, an anti‐Fc, or an anti‐CLEC‐2 polyclonal antibody were immobilized at a concentration of 10 µg/mL on 96‐well plates. After blocking with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS, the plates were incubated with biotinylated NZ‐1 or biotinylated CLEC‐2–Fc chimera at 10 µg/mL, followed by incubation with a peroxidase‐conjugated biotin–streptavidin complex. The enzymatic reaction was conducted with a substrate solution containing TMB (TMB‐Turbo). After the reaction was stopped with 1 M H2SO4, the optical density was measured at 450 nm with an autoplate reader. *P < 0.01 compared to control, by t‐test.
