Figure 1.
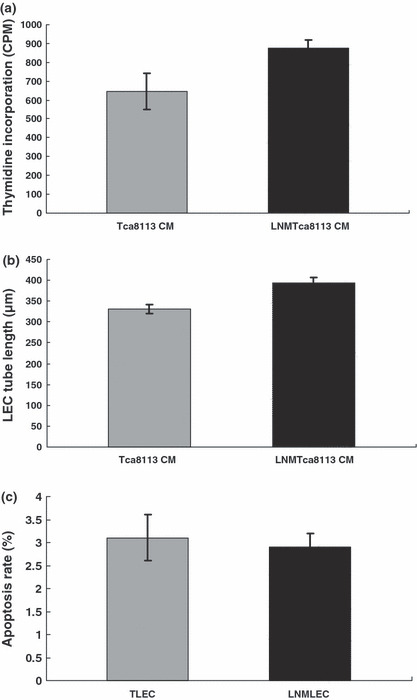
Lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) induced by LNMTca8113 cells and Tca8113 cells displayed different biologic behaviors. (a) LEC proliferation. LEC proliferation was determined by (3H)thymidine incorporation into the cell DNA. In contrast to Tca8113‐stimulated LECs (TLECs), the proliferation activity of LNMTca8113‐stimulated LECs (LNMLECs) increased moderately (P = 0.017). (b) Lymphangiogenesis. By the measurement of the length of tubules, it was confirmed that lymphangiogenesis could be enhanced by addition of LNMTca8113 conditioned medium (CM) (P = 0.012). (c) LEC apoptosis. The number of apoptotic LECs was determined by Annexin V‐PI staining using a FACSCalibur. The results showed that LNMLECs and TLECs were equal in resisting endothelial cell growth supplement (ECGS) starvation‐induced apoptosis (P = 0.701).
