Figure 4: Mouse MAIT cell subsets have distinct metabolic features.
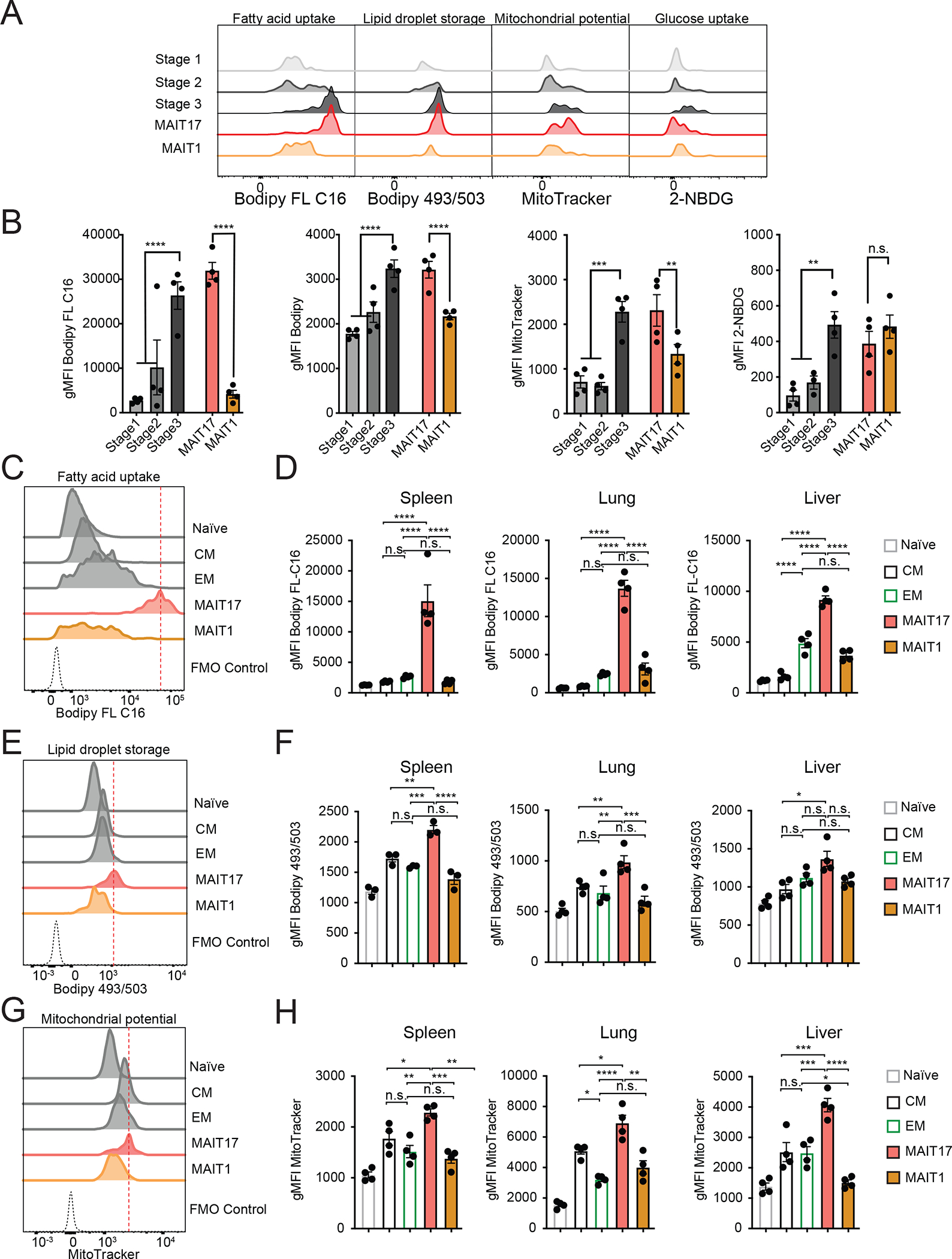
(A-B) Metabolic parameters of MAIT thymocytes were quantified for the thymus MAIT cell differentiation stages 1–3 and mature MAIT1 and MAIT17 thymocytes. Representative histograms (A) and quantification (B) are depicted as geometric mean of fluorescence intensity (gMFI). Neutral lipid droplets were quantified by Bodipy 493/503 fluorescence (left), fatty acid uptake was quantified as intensity of Bodipy FL C16 fluorescence (center left), mitochondrial content was quantified as MitoTracker Deep Red FM fluorescence (center right) and glucose consumption by uptake of 2-NBDG (right). (C-H) Cells were isolated from spleen, lung and liver and metabolic parameters were quantified in CD8+ naïve, central memory (CM) and effector memory (EM) TCRβ+ CD8+ T cells and MAIT cell subsets. Representative histograms (C) and quantification (D) of fatty acid uptake in the indicated cell types. Representative histograms (E) and quantification (F) of neutral lipid droplet content. Representative histograms (G) and quantification (H) of mitochondrial content. Data from 3–4 mice per group, representative of ≥3 experiments. Data analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test for multiple comparisons, displayed as mean± SEM, *P <0.05, **P <0.01 ***P <0.001 and ****P <0.0001.
