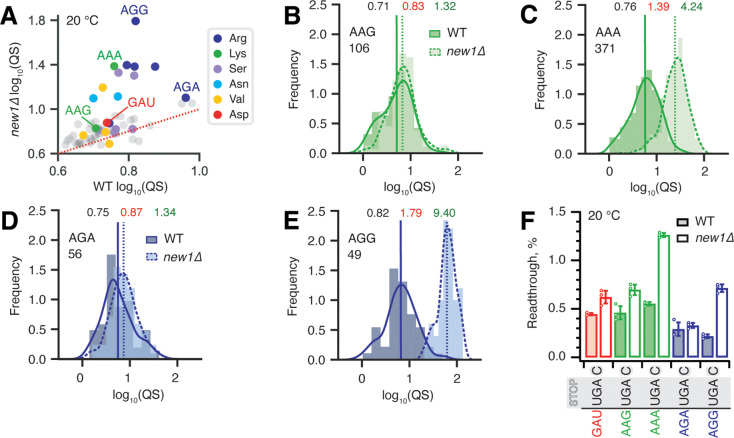
Figure 5. Synonymous codons encoding the C-terminal lysine and arginine residues have dramatically different effects on translation termination defects in new1Δ yeast.
(A) Wild-type and new1Δ QS scores for ORFs parsed by the codon preceding the stop codon. (B-E) QS distributions with ORFs containing C-terminal lysine encoded by either AAG (B) or AAA (C), as well as arginine encoded by either AGA (D) or AGG (E). Wild-type: solid line, darker shading. Δnew1: dashed line, lighter shading. Geomeans of QS distributions for wild-type is black and for new1Δ is in red, the QS fold change is in green. All analyses were performed on pooled dataset from three replicates collected at 20°C. (F) Stop codon readthrough efficiencies of UGA stop codon combined with penultimate codons as indicated on the figure. Error bars represent standard deviations, all experiments were performed at 20°C.