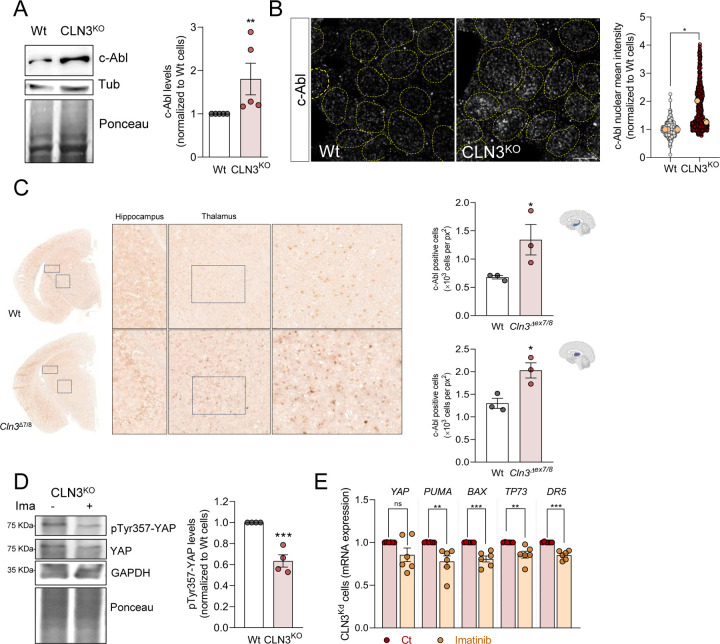
Figure 3. Loss of CLN3 triggers activation of c-Abl.
(A) Representative immunoblot image and quantification of c-Abl protein levels in Wt and CLN3KO cells. Tubulin and Ponceau were used as loading controls. (B) Confocal fluorescence images of HEK293T WT and CLN3KO cells immunostained for c-Abl protein. Nucleus are outlined by the yellow dashed line using Hoechst staining. Scale bar 10µm. On the right, quantification of the mean intensity of c-Abl at the nucleus from at least 100 cells per condition in each independent experiment, with a total of at least 500 cells. The yellow dots represent the mean of each independent experiment. (C) Immunohistochemistry analysis of c-Abl staining of control (Wt) and Cln3Δex7/8 animals; Right panels are cropped images from thalamus; Quantification of the number of positive nucleus to c-Abl in the total area from the hippocampus (upper panel) and thalamus (bottom panel). (D) Representative immunoblot image and quantification of pTyr357-YAP in CLN3KO cells control or treated for 24h with 0.1 µM imatinib (c-Abl inhibitor). GAPDH and Ponceau were used as loading controls. (E) mRNA levels of YAP target genes involved in apoptosis in HEK293T CLN3KO cells untreated or treated for 24h with imatinib. All the results are mean±SEM of at least three independent experiments. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; ***p<0.001. * p<0.05; *** p<0.001; using unpaired t-test.