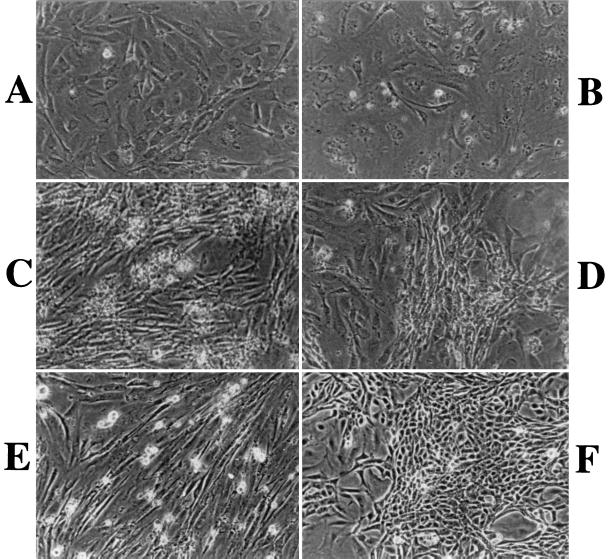
FIG. 4.
LMP1 extends the passage number of MEF cells and induces a morphological transformation of the cells in cooperation with CDK4R24C. (A) P1 MEF cells infected with v-LNSX. (B) P4 MEF cells infected with v-LNSX. Cells are flat and enlarged, indicating that they are approaching senescence. This is the last passage that can be routinely obtained with MEF-LNSX cells. (C) P10 MEF cells infected with v-LMP1. Cells are smaller, with a long spindle shape. They have a higher plating efficiency and grow continuously. (D) P10 MEF cells coinfected with v-LMP1 and v-H-rasV12. Their morphology and growth properties are similar to those of v-LMP1-infected cells. (E) P4 MEF infected with v-CDK4R24C. The cells were further passaged once before they stopped dividing. (F) P10 MEF cells coinfected with v-LMP1 and v-CDK4R24C. The cells exhibit a transforming morphology characterized by smaller and shorter cells with a high density. They are the most actively proliferating cells.