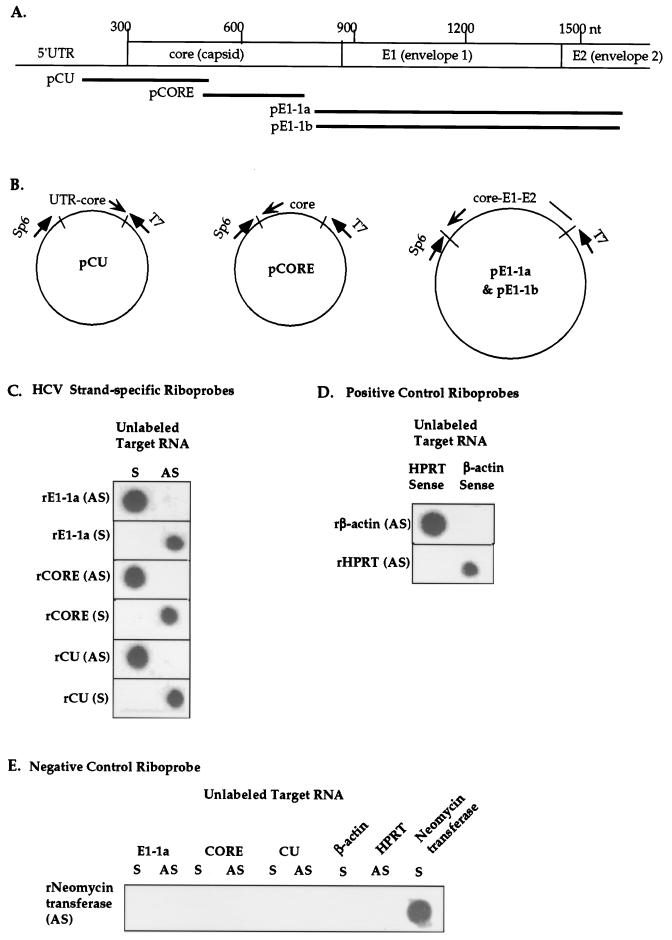
FIG. 1.
Characterization of Dig-labeled riboprobes specific for HCV sense and antisense RNAs. (A) Map location of riboprobes within the HCV genome (see Table 1 for nucleotide positions). Abbreviations: 1a, HCV genotype 1a; 1b, HCV genotype 1b; nt, nucleotide. (B) Recombinant plasmids containing subgenomic fragments of HCV genotype 1a or 1b were constructed for generation of riboprobes by in vitro transcription from bacteriophage T7 or Sp6 promoters. (C) Dot blot assay for assessing the strand specificity of HCV riboprobes. Unlabeled HCV genomic (sense [S]) and replicative-intermediate (antisense [AS]) target RNAs were synthesized by in vitro transcription from recombinant plasmid pE1-1a, pCORE, or pCU (B), treated with DNase I, and blotted onto nylon membranes. Unlabeled target RNAs were hybridized with Dig-labeled riboprobes synthesized from the genomic (S) or antigenomic (AS) strands of the corresponding recombinant DNA templates. For example, rE1-1a (AS), indicates the antigenomic riboprobe corresponding to the HCV genotype 1a E1 gene. (D) Specificity of positive control riboprobes specific for human beta-actin and HPRT sense RNAs. (E) Specificity of negative control riboprobe for Neo. Unlabeled sense (S) RNA probes and Dig-labeled antisense (AS) RNA probes were generated from recombinant DNA templates containing human and bacterial genes and were hybridized in the dot blot assay.