FIGURE 6.
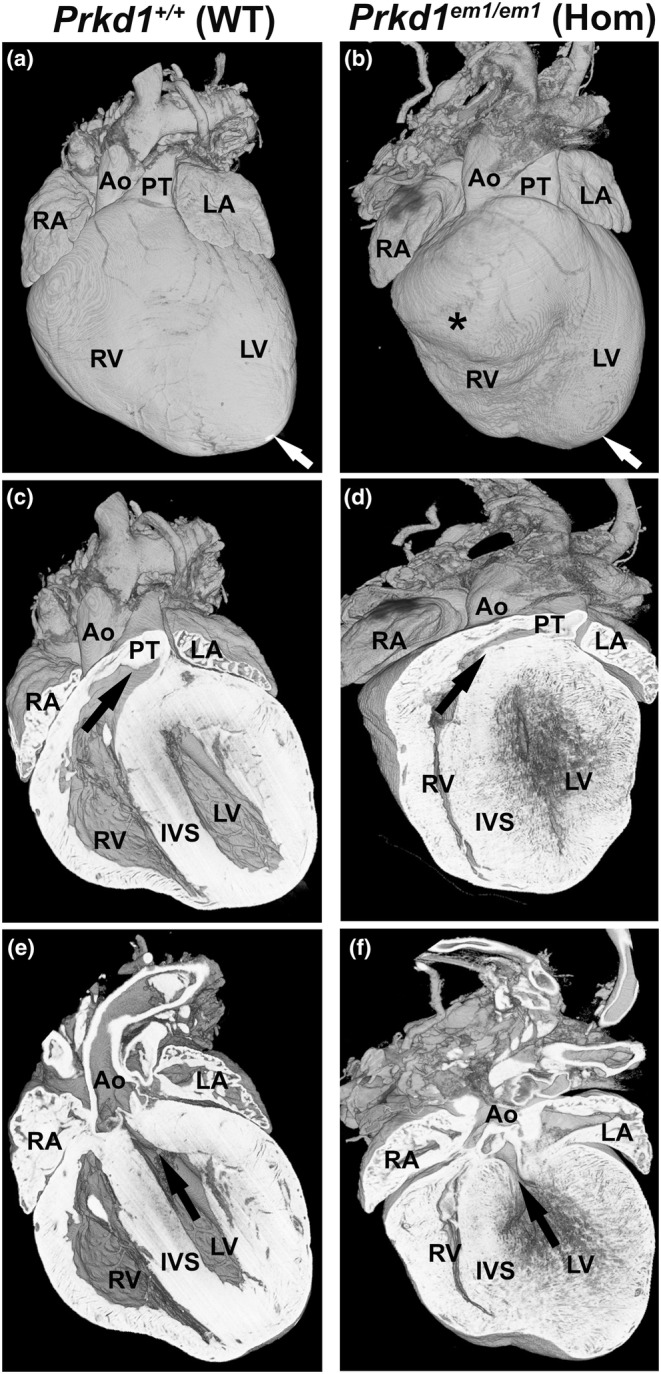
Comparison of Prkd1 +/+ and Prkd1 em1/em1 hearts at P7. (a, b) External view of Prkd1 em1/em1 (homozygous) heart shows that it is smaller and appears to have a more rounded shape and bifid apices (white arrow and asterisk), with the right ventricular apex located ventrally and further to the right in comparison to Prkd1 +/+ (WT) control. (c, d) Ventral view showing a reduced cavity size in the RV body as well as the RV outflow tract, which is longer and more horizontally orientated than in the WT heart (black arrow). (e, f) Coronal sections (ventral view) of the same WT and the homozygous hearts oriented in a plane to show the LV cavity is small with poorly defined endocardial surface and marked myocardial thickening. Even allowing for the heart being ‘empty’ there is an increase in subaortic crowding than in the WT heart, consistent with a left as well as right ventricular outflow tract narrowing. Ao, aorta; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; PT, pulmonary trunk; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle; IVS, interventricular septum; WT, wild type.
