Fig. 5 |. Peripheral endocannabinoids drive exercise performance.
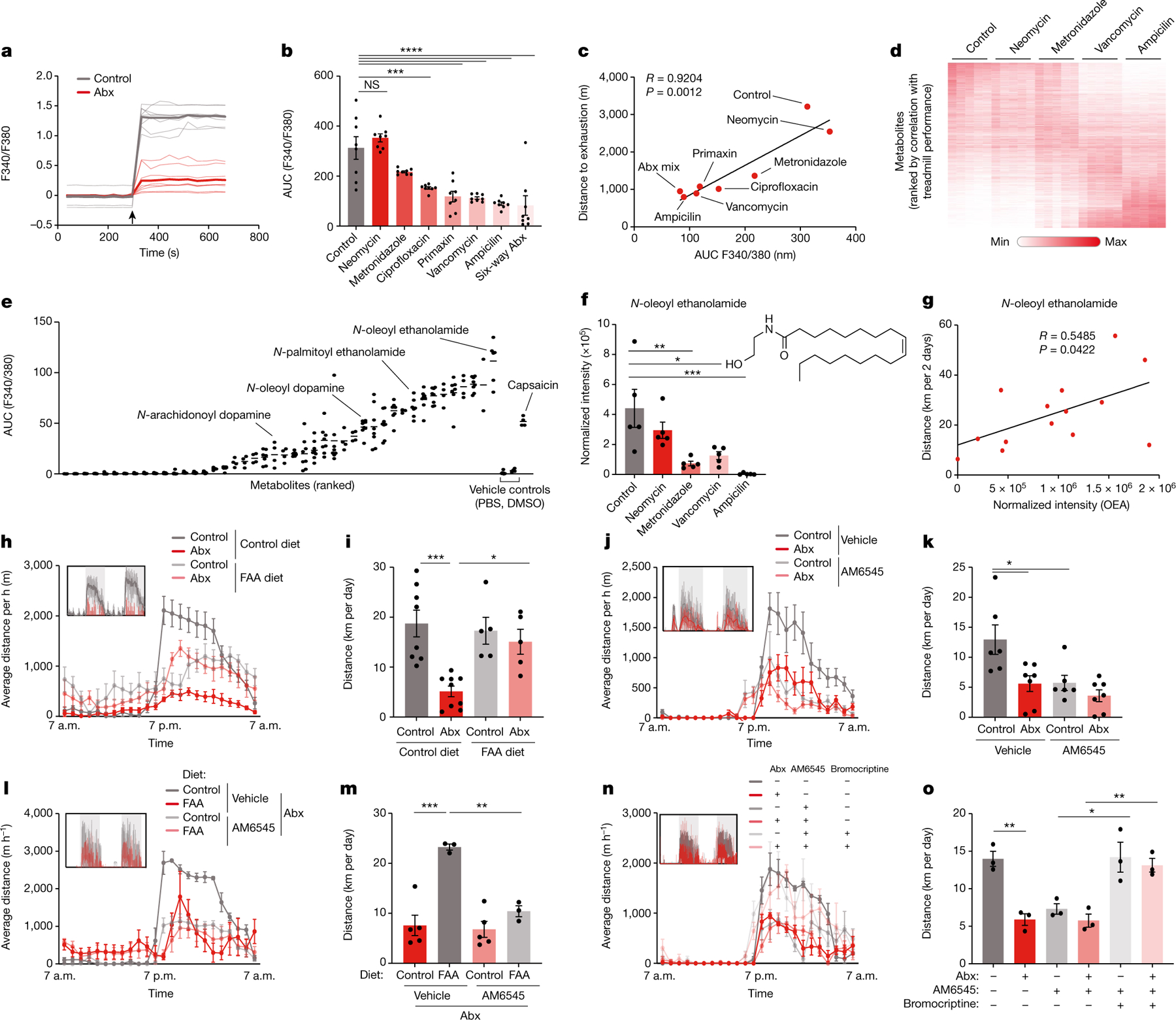
a, Recording traces of calcium imaging of DRG neurons exposed to stool filtrates from Abx-treated mice and controls. Arrow indicates treatment time. b,c, Quantification (b) and correlation with treadmill distance (c) of calcium imaging of DRG neurons exposed to stool filtrates from mice treated with different Abx. Arrow indicates treatment time. d, Heatmap of metabolites detected in caecal contents from mice treated with different Abx. e, Quantifications of calcium imaging of DRG neurons exposed to individual metabolites. f, Normalized abundance of OEA in caecal contents from mice treated with different Abx. g, Correlation between OEA abundance and wheel running in DO mice. h–o, Averaged hourly distance (h,j,l,n) and quantification (i,k,m,o) of voluntary wheel activity of Abx mice and controls, fed a FAA-supplemented or control diet (h,i,l,m), with or without treatment with the peripheral CB1 antagonist AM6545 ( j–o) and the dopamine receptor agonist bromocriptine (n,o). Insets show representative recording traces. Error bars indicate means ± s.e.m. *, P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Exact n and P values are presented in Supplementary Table 2.
