Figure 3.
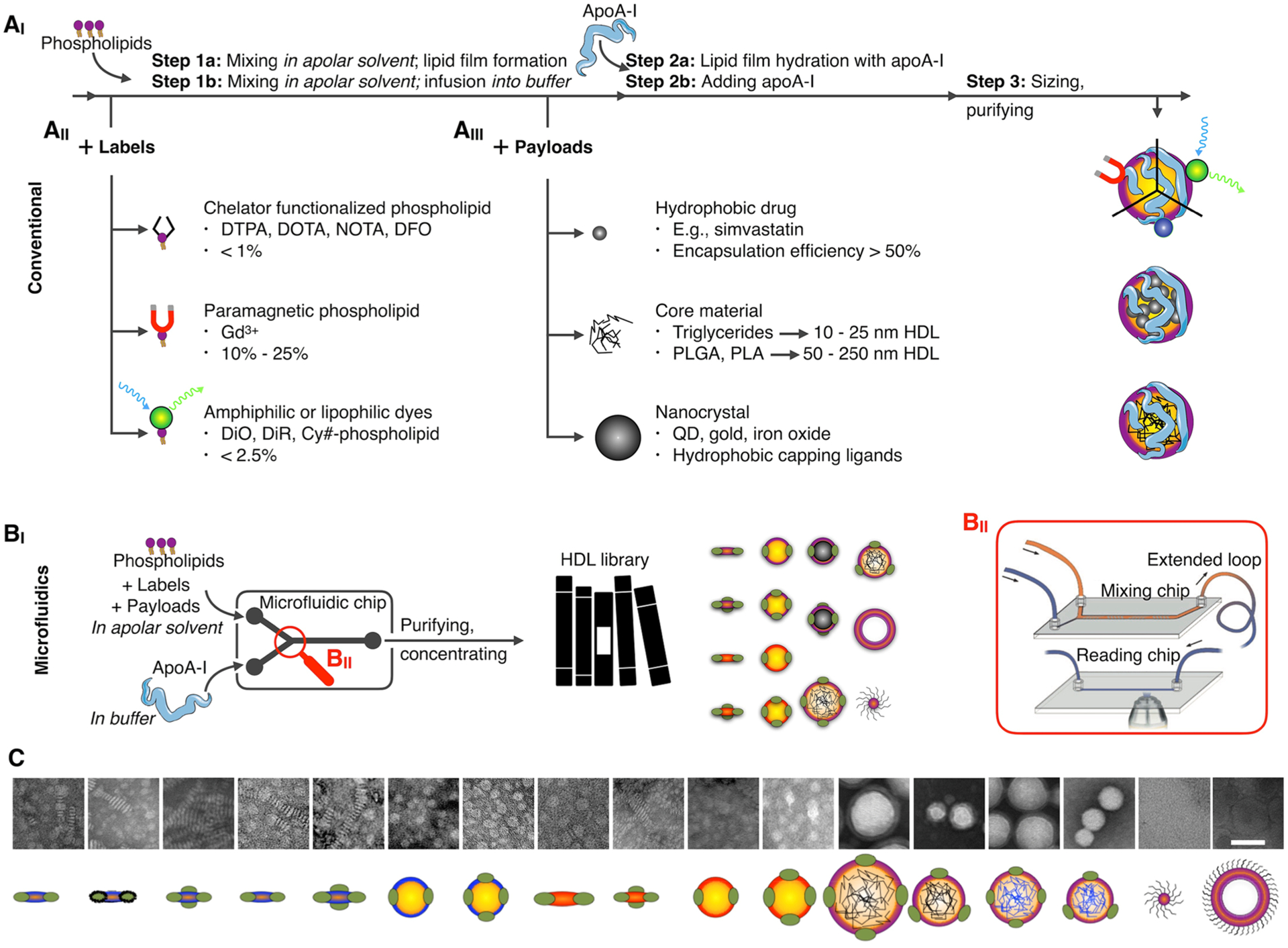
HDL nanobiologics production. (AI) HDL can be reconstituted per different “conventional” strategies and include (AII) amphiphilic labels or (AIII) hydrophobic core payloads. (BI) Microfluidic technology allows HDL nanobiologic instantaneous formation, (BII) a process that can be monitored by FRET confocal microscopy (reproduced with permission from ref 24; copyright 2017 Wiley). Judicious control over solvents, reagent concentration, infusion speeds, and microfluidic chip design facilitates establishing nanobiologic libraries. (C) Transmission electron micrographs (scale bar 50 nm) and schematic representations of HDL nanobiologic library. Adapted with permission from ref 15. Copyright 2016 National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
